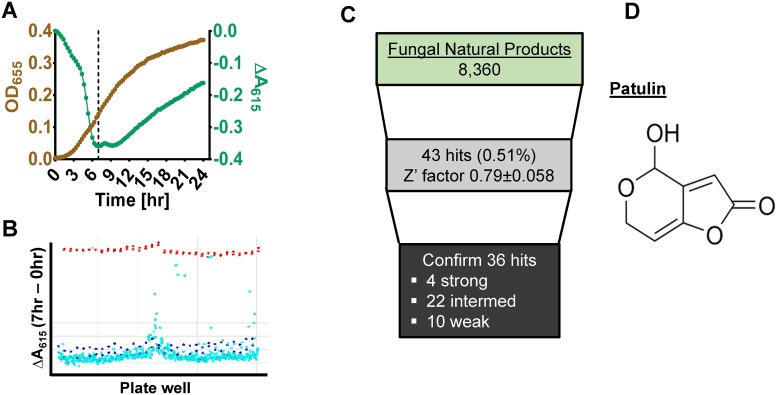
Fig 1. A high-throughput screen based on bacterial fermentation identifies fungal extracts active against multidrug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae.
The antibacterial natural product is patulin. A, Correlation between bacterial growth measured by optical density (OD655) and color change of the medium as a result of bacterial fermentation of mannose (ΔA615). The nadir of the color change occurs at early- to mid-exponential growth and is indicated by the dashed line. B, Representative data from two screen plates with ΔA615 (y-axis) plotted against well location (x-axis). Red circles indicate the measurement using gentamicin as a positive control. Dark blue circles indicate negative controls (medium with no antimicrobials). Light blue circles indicate sample wells that contain unknown compounds. C, Summary of the outcomes from the fungal extract library screened. Patulin was a component of all strong hits. D, The chemical structure of patulin.