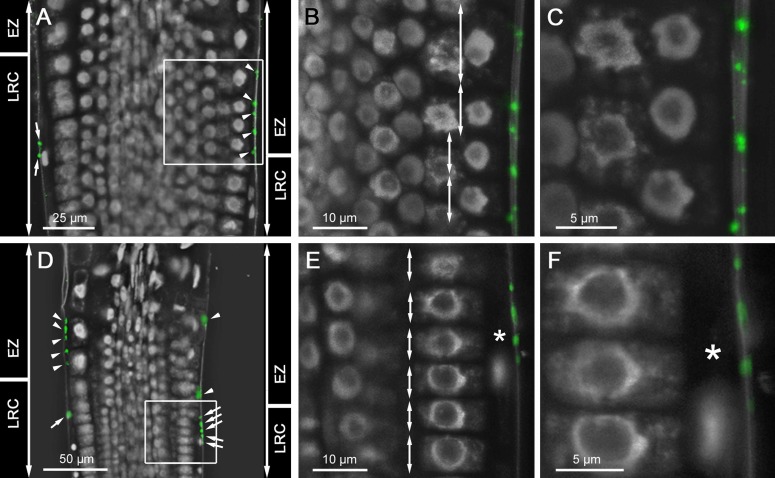
Fig 9. CEP2 is immunolocalized to root cap corpses sticking to epidermis cells in the rapid elongation zone.
(A and D) Two root tips of 10 days old WT seedlings incubated with anti-CEP2 peptide antibody and cyanine CY2-coupled secondary antibody are analyzed by CLSM (Leica SP8). Nuclei are characterized by their strong white auto fluorescence, whereas other parts of the cell are barely fluorescing and look black. (A-C) is focusing on epidermis cells of the elongation zone (EZ), whereas (D-F) is focusing on cells at the upper end of the LR cap (LRC) with two different magnifications of the white boxed area in (B-C) and (E-F), respectively. LR cap cells are long and small with one single nucleus (see asterix in E and F), whereas epidermis cells are short at the level of the LR cap and are elongating at the level of the rapid elongation zone (compare double arrows in B and E). CEP2 signals (green) are exclusively found in LR cap cells (see arrows in A and D) and in root cap corpses sticking to the cell wall of epidermis cells at the beginning elongation zone (see arrow heads in A and D).