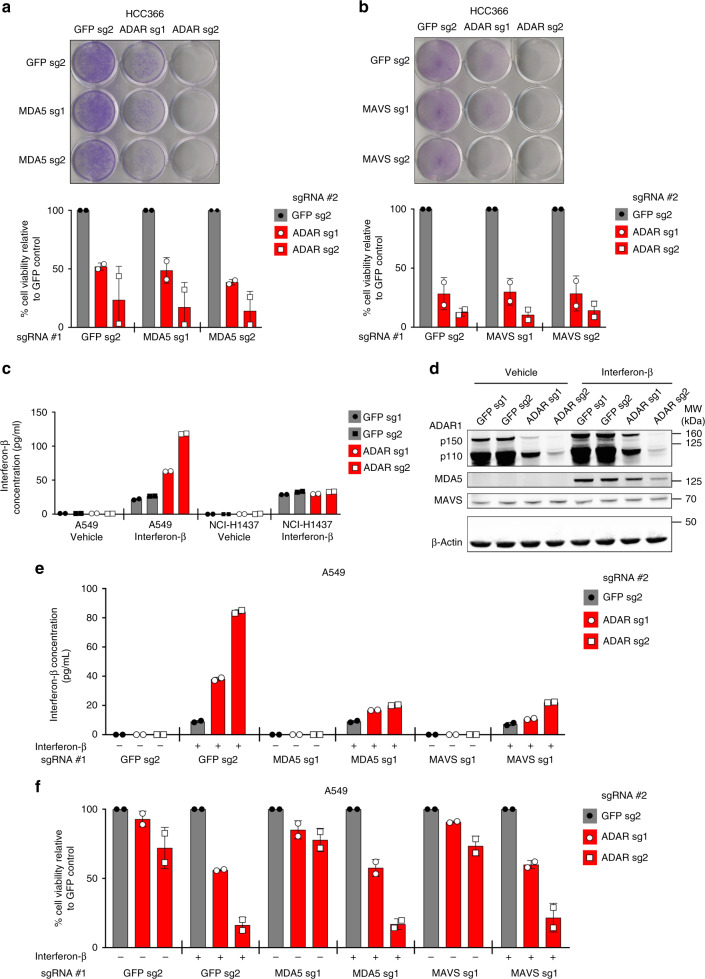
Fig. 2.
MDA5 and MAVS are required for IFN-induced IFN-β production, but not cell lethality, after ADAR deletion. a, b Cell viability of control and MDA5-deficient (a) or MAVS-deficient (b) HCC366 cells was assessed by crystal violet staining 8–13 days after GFP or ADAR KO with CRISPR-Cas9. A representative image of crystal violet staining (top) and quantitation of cell viability (bottom) from two independent biological replicates (for both a and b) are shown. Cell viability values were normalized to the GFP sg2 control #2 within each group of isogenic cell lines. c IFN-β secretion by control or ADAR1-deficient A549 cells was measured by ELISA after treatment with either vehicle or IFN-β (10 ng/mL) for 24 h. NCI-H1437 cells harbor a homozygous deletion of the IFNB1 locus. Technical replicates from one representative experiment are shown. Three independent biological replicates were performed for A549 cells and one experiment was performed for NCI-H1437 cells. d Immunoblots showing MDA5 and MAVS protein levels in control (GFP sgRNAs) and ADAR1-deficient A549 cells 24 h after treatment with vehicle or IFN-β (10 ng/mL). β-Actin served as a loading control. One representative immunoblot from two independent biological replicates is shown. e IFN-β secretion by the indicated A549 cells was measured by ELISA after treatment with vehicle or IFN-β (10 ng/mL). Technical replicates from one representative experiment out of two independent biological replicates are shown. f Cell viability of the indicated A549 cells from e was assessed by cell counting 2 days after treatment with vehicle or IFN-β (10 ng/mL). Cell viability values were normalized to the GFP sg2 control #2 within each group of vehicle or IFN-β-treated isogenic cell lines. Two independent biological replicates are shown. Error bars represent standard deviation in all graphs