Fig. 3.
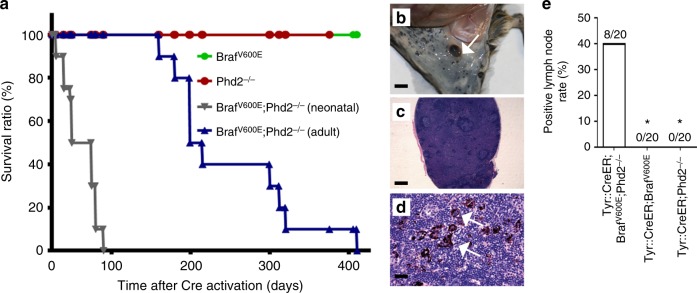
Survival and lymph node metastasis in Tyr::CreER;BRafV600E;Phd2−/− mice. a Kaplan–Meier survival analysis of Tyr::CreER;BRafV600E (n = 20), Tyr::CreER;Phd2−/− (n = 20), Tyr::CreER;BRafV600E;Phd2−/− postnatal mice (n = 20) and Tyr::CreER;BRafV600E;Phd2−/− adult mice (6 weeks, n = 20) after 4-OHT induction. Log rank tests of survival plots of the data indicated a statistically significant difference between the following survival curves: Tyr::CreER; BRafV600E; versus Tyr::CreER;BRafV600E;Phd2−/− mice (p < 0.0001), and Tyr::CreER;BRafV600E;Phd2−/− adult versus Tyr::CreER;BRafV600E;Phd2−/− postnatal mice (p < 0.0001). b–d Lymph node metastasis in Tyr::CreER;BRafV600E;Phd2−/− mice. A positive lymph node was present near the area with melanoma induction (arrow points to the lymph node, b). The lymph node was enlarged with pigmented cells (c) and high-power view showed melanoma cells in the lymph node (arrows point to the tumor cells, d). e Percentage of mice that developed lymph node metastasis. Bar in c indicates 200 μm. Bar in d indicates 50 μm. Bar in b indicates 3 mm. *p < 0.05 compared to Tyr::CreER;BrafV600E;Phd2−/− group using one-way ANOVA with pairwise comparisons