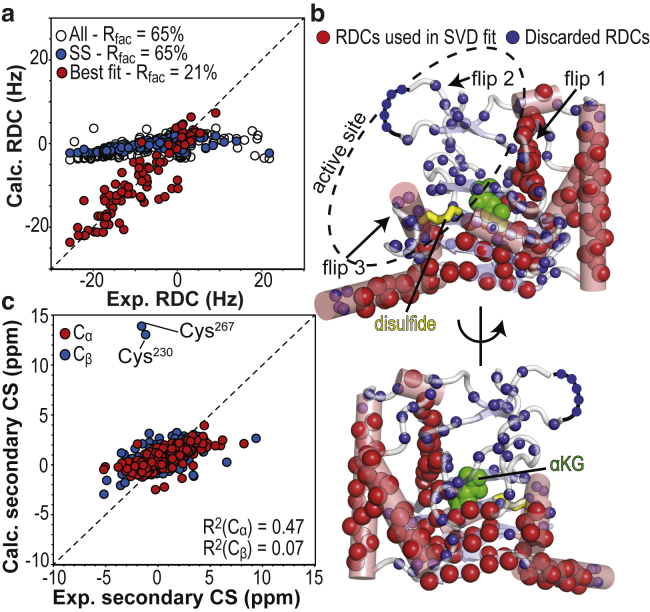
Figure 1.
Comparison of the x-ray structure of apo Alkbh5 with solution NMR data. (a) Agreement between the observed and calculated RDCs obtained by SVD to the coordinates of the x-ray structure of apo Alkbh5 (PDB: 4NJ4 (21)). SVD fitted using the full set of experimental RDCs (open black circle) or RDCs from backbone amides in secondary structures (blue circles) fails to converge (because of the lack of a single orientation of the alignment tensor that satisfies all the experimental data), resulting in predicted RDC values close to zero and high R-factors (see Table 1). Exclusion of RDCs from the protein active site from the SVD analysis results in good agreement between experimental and back-calculated RDCs (red circles). (b) Amide groups whose experimental RDCs are in good agreement with back-calculated values are shown as red spheres on the x-ray structure of apo Alkbh5. Smaller blue spheres indicate the location of RDCs that were not included in the final SVD analysis (i.e., RDCs from loop or active-site residues). Residues that are missing from the x-ray structure (Leu145–Gly149) are indicated by a black curve. The Cys230–Cys267 disulfide bridge is shown as yellow sticks. αKG is modeled in the protein active site and shown as green spheres. (c) Agreement between measured and back-calculated Cα/Cβ secondary chemical shifts. Back-calculation of the NMR chemical shifts was done using Sparta+ (67) and the crystal structure of apo Alkbh5 (21). R2 values for linear regression of the Cα and Cβ data are shown. To see this figure in color, go online.