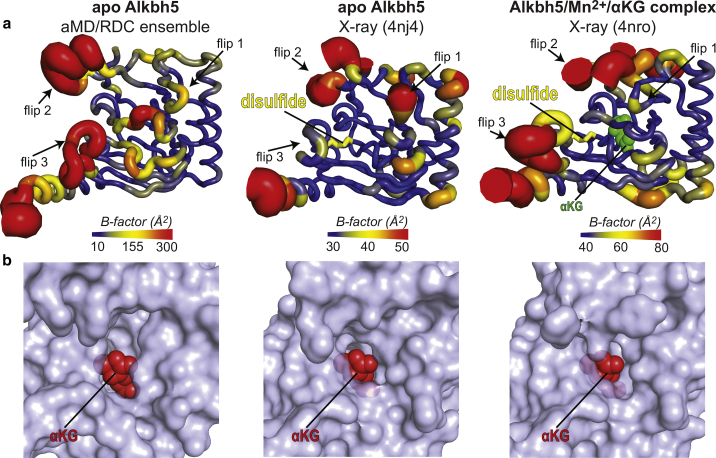
Figure 7.
Comparison between solution and crystal structures of human Alkbh5. (a) Sausage representations of the aMD/RDC ensemble (left), x-ray structure of apo Alkbh5 (center), and x-ray structure of Alkbh5 complexed with Mn2+ and αKG (right). Cartoons are colored according to the B-factor, as indicated by the color bar. B-factors for the aMD/RDC ensemble were calculated using the formula , where Bi and Ui are the B-factor and mean-square displacement of atom i, respectively. The Cys230–Cys267 disulfide bridge is shown as yellow sticks. αKG is shown as green spheres. (b) Close-up views of the αKG binding pocket in the aMD/RDC ensemble (left), x-ray structure of apo Alkbh5 (center), and x-ray structure of Alkbh5 complexed with Mn2+ and αKG (right). For the aMD/RDC ensemble, the conformer with the widest αKG binding pocket is displayed. One αKG molecule is modeled in the binding site of the apo protein (left and center panels). Alkbh5 is shown as a transparent light blue surface. αKG is shown as red spheres. To see this figure in color, go online.