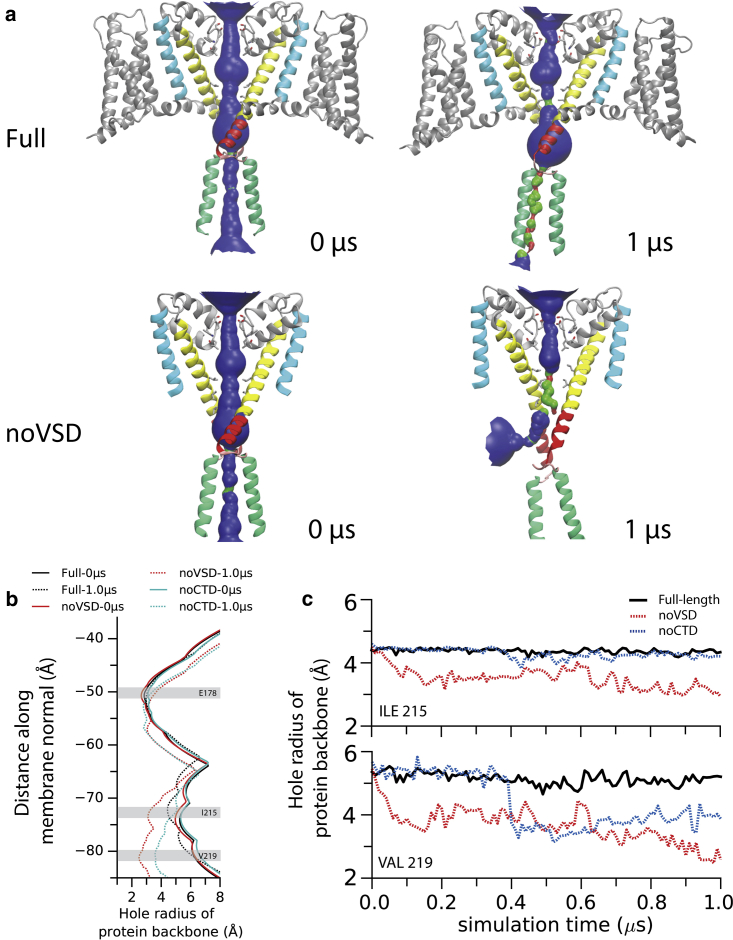
Figure 7.
(a) View of the pore at the start (0 μs) and end (1 μs) of the simulations for the full and noVSD structures. The solvent-accessible volume (by side chain) of the interior of the pore is depicted by HOLE (52) calculations (color code for the radius: red, hole radius < 1.15 Å; green, hole radius < 2.30 Å; blue, hole radius > 2.30 Å). The small thinning of the pore at the hydrophobic region above the gate, leading to the hydrophobic gating, can be seen in the full structure. The collapse of the gate is visible in the noVSD simulation. (b) The interior radius of the pore for protein backbones between the beginnings and ends of the simulations. The shaded area depicts key residues in the selectivity filter (E178) and the gate region (I215 and V219). (c) A comparison of residues’ backbone radii (I215 and V219) over time between full-length, noVSD, and noCTD construct simulations. To see this figure in color, go online.