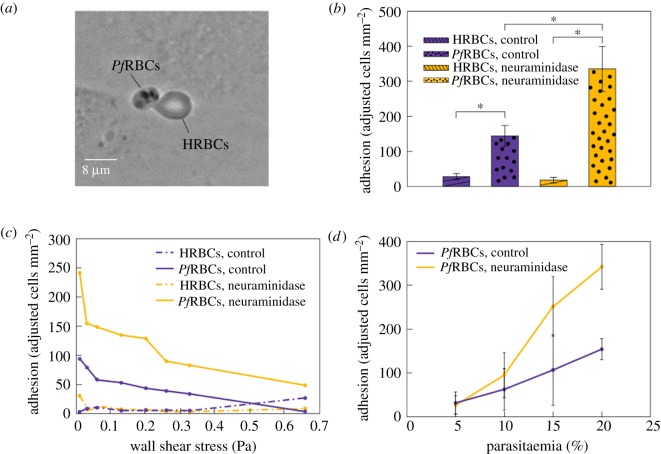
Figure 4.
The effect of HRBC and PfRBC adhesion on HUVEC glycocalyx, before and after the removal of glycocalyx sialic acids with neuraminidase. (a) Snapshot of HRBCs and PfRBCs adhering to HUVEC layer after washing out unattached cells. (b) PfRBC adhesion efficiency is double in neuraminidase-treated endothelium with respect to the control (p < 0.001). PfRBCs always adhere significantly more than HRBCs for control and neuraminidase-treated samples (p < 0.001), while the sialic acid removal of HUVEC glycocalyx has no impact of HRBC adherence. Adjusted adhesion indicates the number of RBCs per mm2 attached to HUVECs normalized by the ratio of PfRBCs and HRBCs. (c) PfRBC adhesion efficiency decreases for increasing wall shear stresses for both control and neuraminidase-treated samples, while HRBC adhesion efficiency remains almost constant for both these conditions. RBCs were classed as adhered to the endothelium when they remained completely attached for about 500 frames for every value of shear stress. (d) Linear increase of PfRBC adhesion as function of parasitaemia for both control and neuraminidase-treated samples. SD from 10 different fields of view per value of parasitaemia.