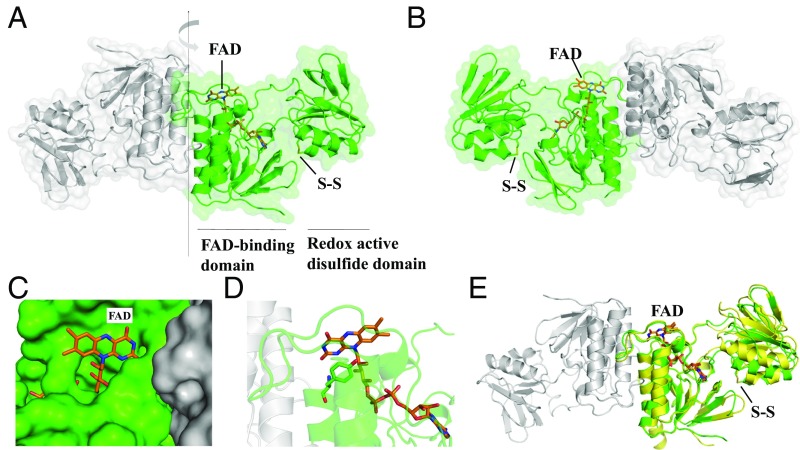
Fig. 1.
Crystal structure of C. acetobutylicum FFTR. (A) A ribbon drawing representation with semitransparent surface of the CaFFTR2 homodimer, with each monomer colored in green and gray. The two domains in one monomer are indicated, with the FAD cofactor and the disulfide shown as sticks. (B) A 180°-rotated view of A as indicated by the arrow in A, favoring the visualizing of the domain organization in FFTR. (C) FFTR is represented in surface, and FAD cofactor is shown in sticks (same view as in B). (D) Close-up view of the interaction between Tyr263 and the isoalloxazine ring of the flavin cofactor. (E) Superposition of FFTR1 (yellow) and FFTR2 (green). For the structural alignment, only the coordinates of the FAD-binding domain were matched. One monomer of FFTR1 is presented for simplification. The flavin and the redox-active Cys amino acids are depicted in stick representation.