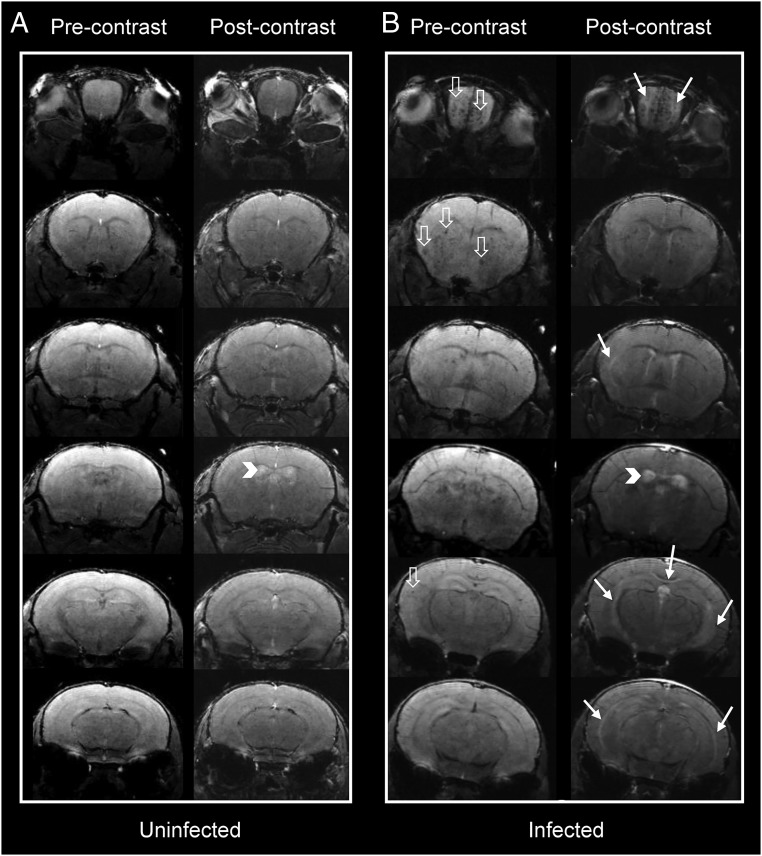
Fig. 3.
Pre- and postcontrast coronal T1 images at different planes in the mouse brain. Representative cross-sectional pre- and postcontrast T1-weighted images in (A) an uninfected and (B) an infected mouse. Postcontrast images in the infected animal show increased signal intensity (solid white arrows) in the olfactory bulbs, underneath the corpus callosum, and external capsules. Physiologic contrast leakage into the ventricular system is seen in the uninfected animal due to prolonged imaging time. Ventricular contrast leakage in the infected animal is more marked, suggesting blood–CSF barrier disruption (arrowheads). Multiple microhemorrhagic changes are seen in the infected animal (hollow white arrows).