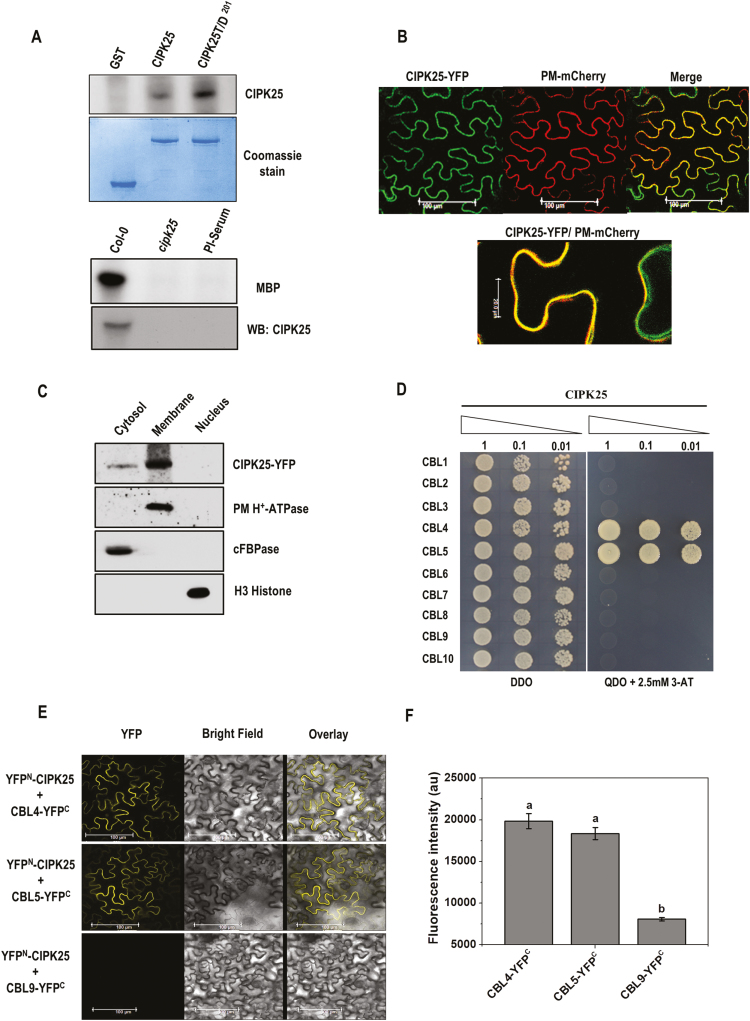
Fig. 3.
CIPK25, an active protein kinase, interacts with CBL4 and 5 in planta. (A) Autophosphorylation assay of bacterially expressed GST–CIPK25 and CIPK25T/D201 proteins. Below is the Coomassie blue-stained gel. The lower panel shows substrate phosphorylation of MBP by immunoprecipitated CIPK25 protein from Col-0 and cipk25 mutant seedlings. Western blot of CIPK25 is shown. (B) Visualization of CIPK25–YFP fusion protein in agroinfiltrated leaves of N. benthamiana co-infiltrated with the plasma membrane marker PM-mCherry. The magnified view of the merged image in the lower panel shows CIPK25 localization at the plasma membrane and cytoplasm. (C) Western blot showing subcellular fractions of CIPK25–YFP-expressing N. benthamiana leaves. The blot was probed with antibodies against GFP for CIPK25, plasma membrane (PM) H+-ATPase, cytosolic fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (cFBPase), and H3 histone. (D) Yeast two-hybrid interaction study of CIPK25 and CBLs. Y2H gold yeast cells were co-transformed with pGBKT7-CIPK25 and pGADT7-CBL1-10, and auxotrophic selection was carried out to detect protein–protein interaction. (E) Interactions between CIPK25 and CBL4/CBL5 in planta were shown by BiFC assay. CIPK25 fused with the N-terminal domain of YFP (YFPN) and CBL4/CBL5/CBL9 fused with the C-terminal domain of YFP (YFPC) were transiently expressed in N. benthamiana by agroinfiltration. Images show YFP-mediated fluorescence derived from the protein–protein interaction. Scale bar=100 µm. Infiltration of CBL9–YFPC with YFPN–CIPK25 was used as the negative control. Expression of the proteins is shown in Supplementary Fig. S1. (F) Fluorescence intensity within leaf discs expressing YFPN–CIPK25 with CBL4–YFPC, CBL5–YFPC, or CBL9–YFPC. Different letters denote significant differences among samples based on Student–Newman–Keuls test (n=8, ANOVA; P≤0.05).