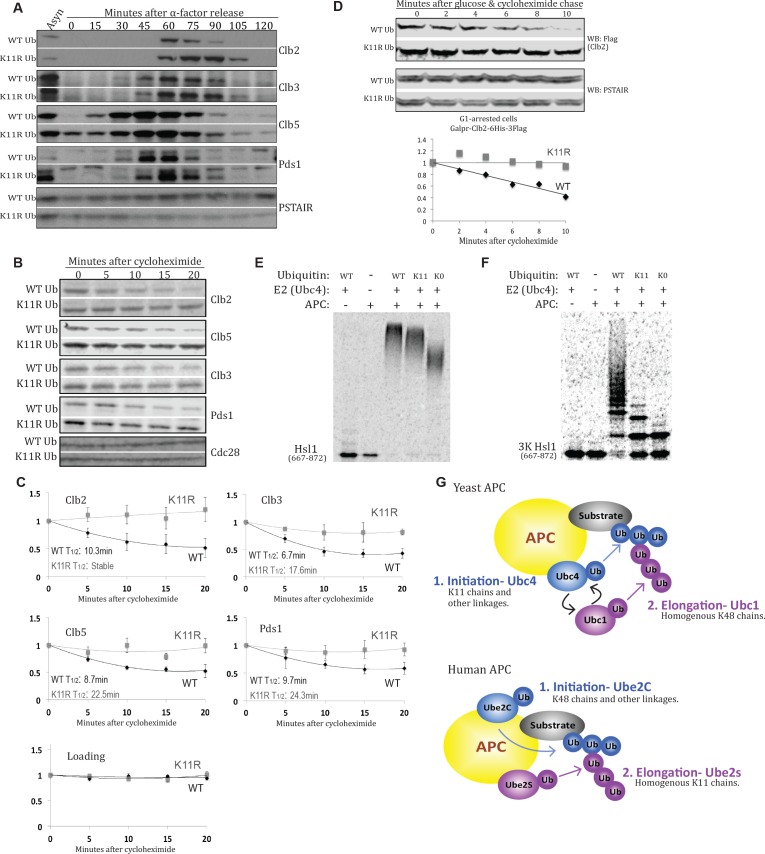
Figure 4. K11 linkages contribute to APC-substrate turnover.
(A) Wild type and K11R ubiquitin mutant cells lacking Cdc26 were synchronized in G1 phase with α factor, then released into the cell cycle. Samples were taken at the specified times after release and analyzed by probing western blots for the indicated proteins. (B, C) cdc26Δ cells expressing wild type or K11R ubiquitin were arrested in G1 with α-factor. Cells were washed in fresh media to release from the arrest and, after sixty minutes, protein synthesis was blocked by the addition of cycloheximide. The APC was active at this time point, as measured by Pds1 and Clb5 turnover (Panel 4A). Samples were taken at the specified times after cycloheximide addition and analyzed by probing western blots for the indicated proteins. Bands were quantified using the Licor Image Studio Software and were normalized to Cdc28 or PSTAIR as loading controls (n = 3). A second order polynomial best-fit line was calculated. Half lives were calculated by determining the slope of the line tangent to the best fit curve at T = 0. (D) Cells were synchronized in G1 phase with α factor. During the G1 arrest, Clb2-6xHis-3xFlag expression was induced by the addition of galactose, and cells were shifted to 37°C. Clb2 synthesis was then blocked by removal of galactose, and addition of glucose and cycloheximide. The levels of Clb2-6xHis-3xFlag in wild-type and K11R ubiquitin cells lacking Cdc26 were analyzed by western blotting at the indicated times. Cdc28 was examined as a loading control using Anti-PSTAIR antibody. Bands were quantified as in Figure 4C. (E) A radioactively labeled fragment of Hsl1, amino acids 667–872, was incubated with or without APC/Cdh1, Ubc4, and different forms of ubiquitin, as indicated. The ubiquitination of Hsl1 was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. (F) All lysine residues on Hsl1 (667-872) were mutated to arginine, except for two lysines (K775, 812) that are part of 2 KEN box degrons, and lysine 747, which has been previously reported as being ubiquitinated. This Hsl1 fragment is termed Hsl1-3K, and was analyzed as in 4E. (G) A model describing the well-established role of K11 linkages in mammalian cells, and their function in yeast APC substrate degradation as suggested by the data presented here.
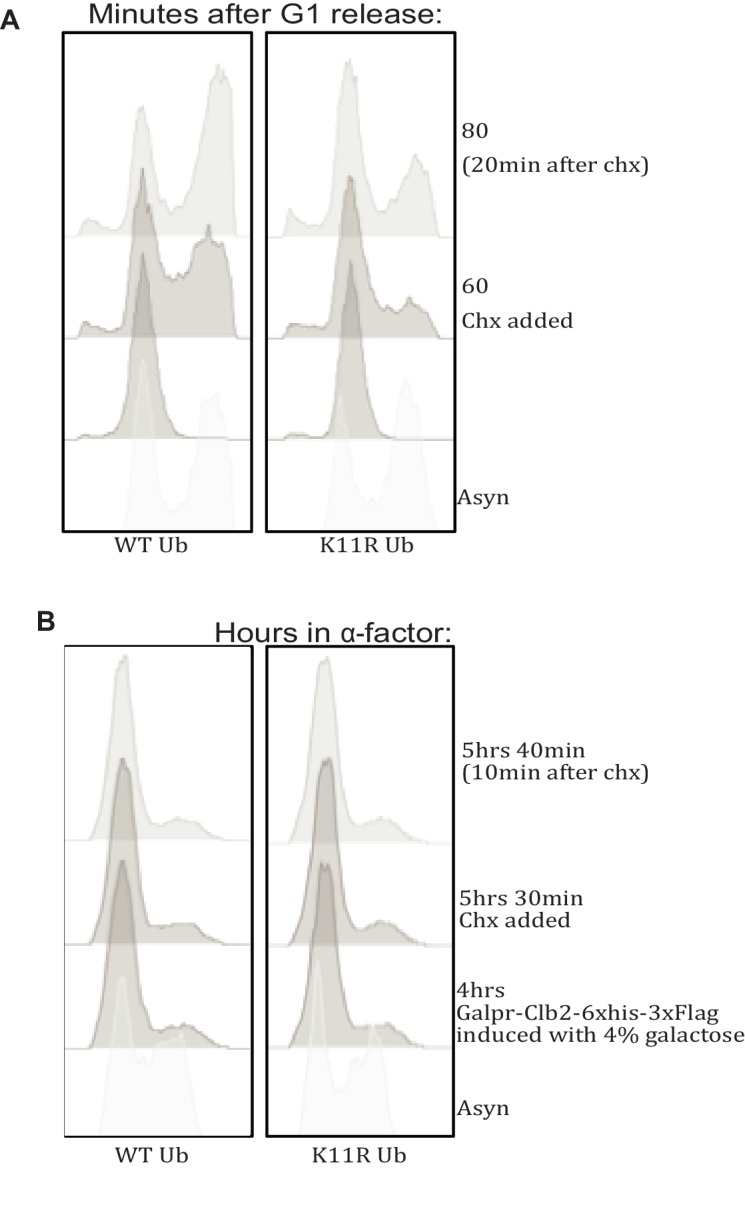
Figure 4—figure supplement 1. Cell cycle profiling by FACS.