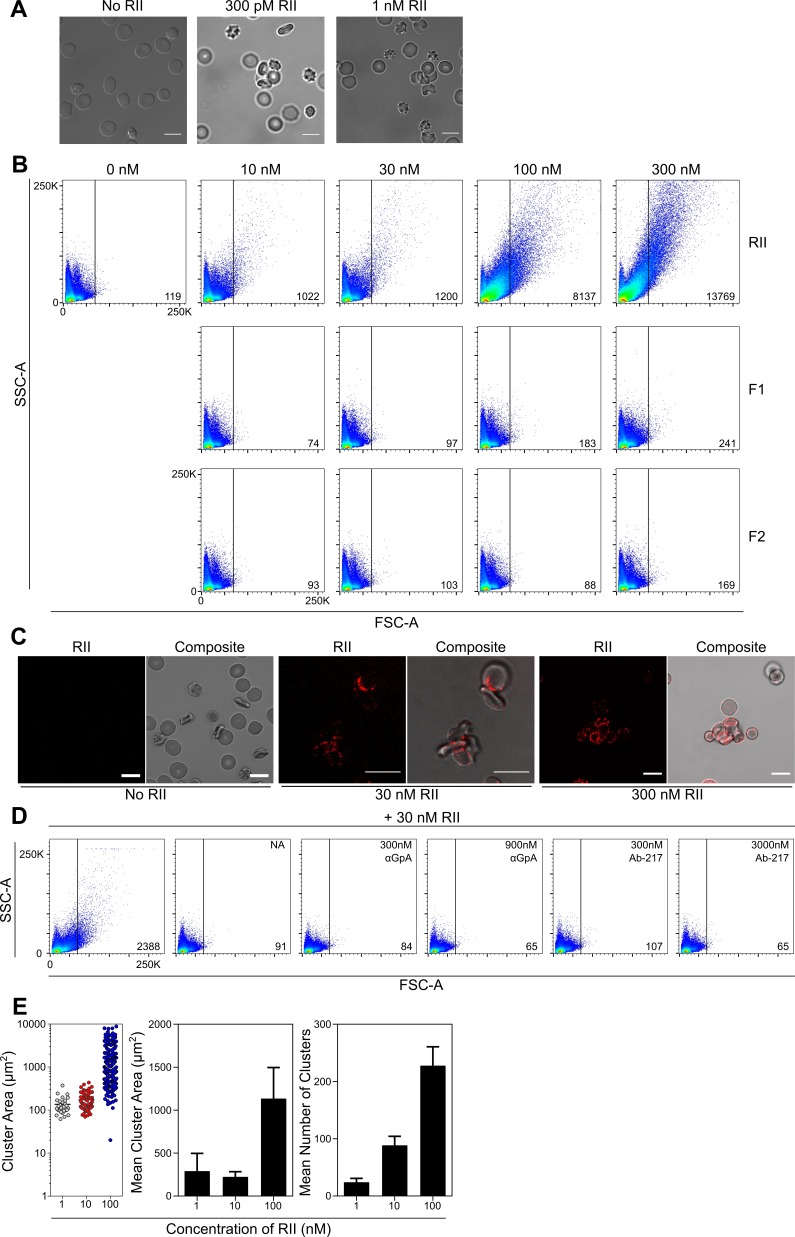
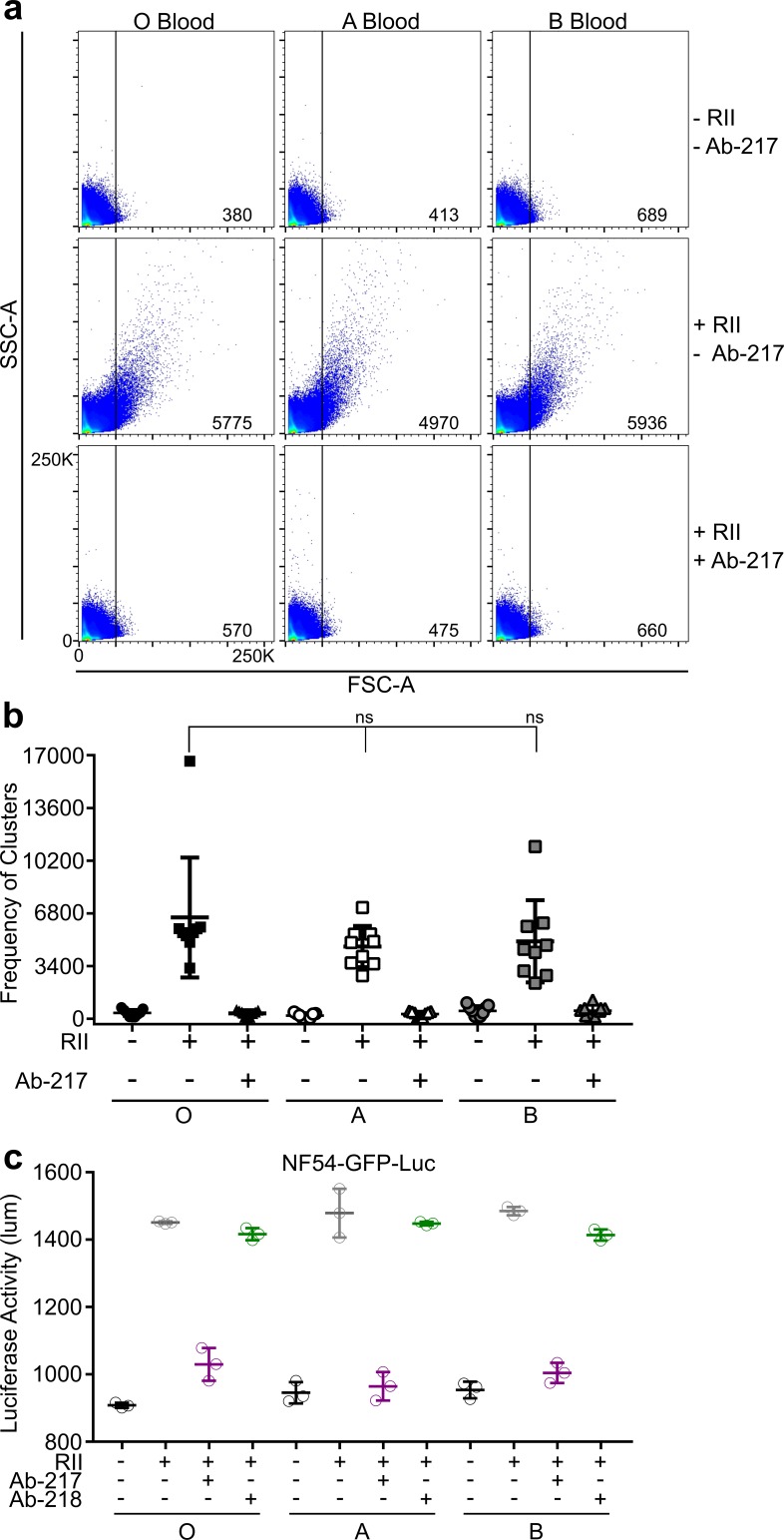
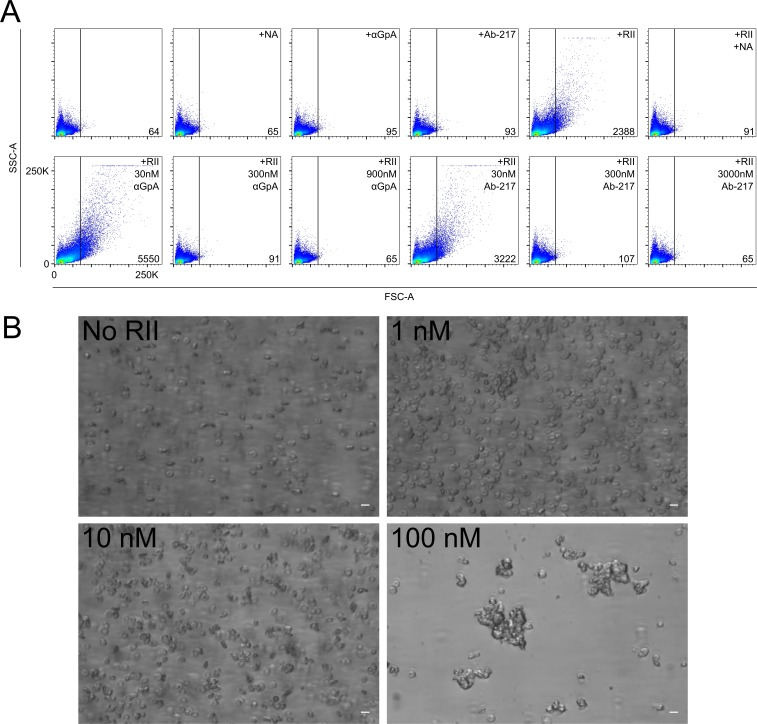
Figure 2. EBA-175 RII binds and promotes RBCs to form clusters through interactions with GpA.
(A) Clustered RBCs adhere to one another via RII at 300pM and 1 nM concentrations. Scale bars are 10 µm. (B) RII, but not the individual DBL domains F1 or F2, induces RBC clustering in a concentration dependent manner as observed by FSC-A. Frequency of events (clusters) out of 100,000 counts are located in bottom right corner of dot plot for each sample when gated according to the no protein control (top left). One representative biological replicate out of three is presented. (C) Clustered RBCs adhere to one another via RII at the interface between each red cell. Scale bars are 10 µm. (D) Inhibition of particle size shift of RBCs incubated with RII by neuraminidase (NA, panel 2), anti-GpA Ab (panel 3 and 4), and anti-RII Ab-217 as observed by FSC-A (panel 5 and 6). Frequency of events (clusters) out of 100,000 counts are located in bottom right corner of dot plot for each sample when gated according to the no protein control (top left). One representative biological replicate out of three is presented. (E) Analysis of cluster size for varying concentrations of EBA-175 RII under flow conditions of 1 dyn/cm2. Left hand panel shows representative data from one experiment. Each circle represents a single cluster area (µm2). Middle panel shows mean cluster size for each concentration, and right hand panel shows mean number of clusters per concentration for three independent experiments ± S.D.