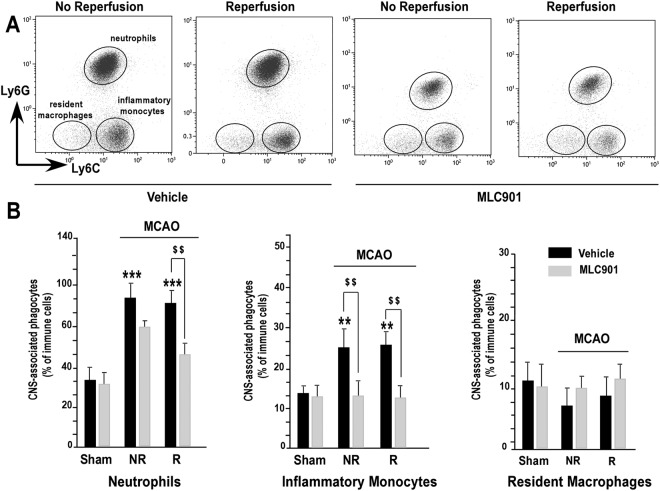
Figure 3.
MLC901 reduced the infiltration of neutrophils and inflammatory monocytes induced by focal 60-min ischemia in mouse brains. (A) Representative bivariate dot plots of CNS-phagocytes stained for Ly6G and Ly6C illustrating a gating strategy to identify Ly6Cintermediate+/Ly6Ghigh+ neutrophils, Ly6C−/Ly6G− resident macrophages and Ly6Chigh+/Ly6G− inflammatory monocytes. (B) Histograms of average percentage of neutrophils (left), inflammatory monocytes (middle) and resident macrophages (right) in CNS-associated phagocyte cell population from reperfused (R) or not reperfused (NR) brains of mice submitted to 60-min focal ischemia and treated with vehicle (black bars) or MLC901 (ip injection, 40 μg/kg) (n = 6 to 10 per experimental group) and sacrificed 24 hours after MCAO. Data are reported as mean ± SEM. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 versus sham-operated group and $$P < 0.01 versus vehicle ischemic group (Kruskal-Wallis test, H(4,56) = 23.16).