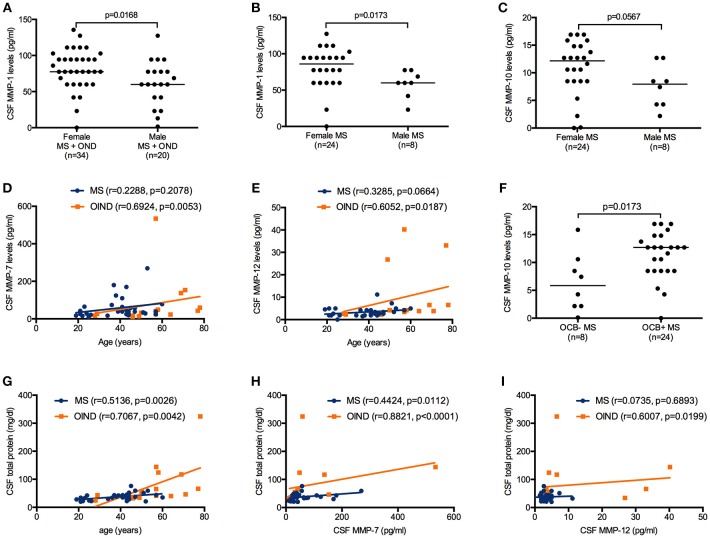
Figure 1.
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) levels in patients affected by multiple sclerosis (MS) and by other inflammatory neurological diseases (OIND) considered as a whole and classified according to clinical diagnosis and clinical features. MMP-1 levels were higher in female than in male patients considered as a whole (Mann–Whitney; p = 0.0168, (A). MMP-1 levels were increased in female than in male MS patients (Mann–Whitney; p = 0.0173) (B). MMP-10 levels were more elevated in female than in male MS patients, however the p value did not reach the significance (Mann–Whitney; p = 0.0567) (C). MMP-7 and MMP-12 concentrations were positively correlated to age in the overall sample (Spearman; r = 0.2920 and p = 0.0321, r = 0.5674 and p < 0.0001, respectively) and in the OIND group (Spearman; r = 0.6924 and p = 0.0053, r = 0.6052 and p = 0.0187, respectively) (D,E). MMP-10 levels were higher in MS patients positive for the presence of IgG oligoclonal bands (OCB+) than in negative (OCB-) (Mann–Whitney; p = 0.0173) (F). CSF total protein levels were positively correlated to age in MS and OIND (Spearman; p = 0.0026 and p = 0.0042, respectively) (G). In CSF: MMP-7 and total protein concentrations were positively correlated in MS and OIND (Spearman; p = 0.0112 and p < 0.0001, respectively) (H), while MMP-12 positively correlated to total protein in OIND (Spearman; p = 0.0199) (I). Each point represents a single observation. Horizontal bars indicate medians (A–C,F).