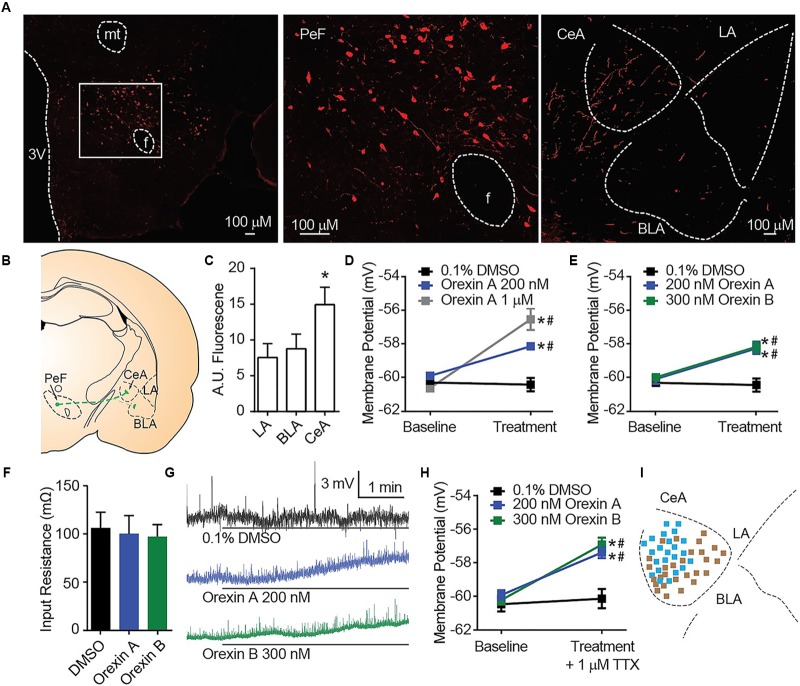
FIGURE 1.
OX mediates postsynaptic depolarization of CeA neurons. (A) Representative 20× images revealed OX A positive cell bodies in the PeF (f is fornix, -2.80 mm bregma) and OX A positive fibers in the amygdala (-2.40 mm bregma). Boxed area is enlarged to show individual OX A-positive PeF neurons. (B) Schematic of PeF projections to the amygdala and (C) summary quantification of fluorescence, n = 7 animals. (D) Depolarization response to OX A was observed for CeA neurons (n = 9–15 cells). (E) CeA neurons depolarized to applications of either OX A or OX B (n = 10–12 cells). (F) Input resistance of CeA neurons before and during OX perfusion. (G) Representative traces of OX mediated depolarization. Solid bars under traces indicate perfusion of OX or vehicle. (H) Depolarization persisted following 1 μM TTX treatment indicating a postsynaptic effect (n = 9–11 cells). (I) Mapping of OX sensitive (blue, 23/51 recordings) and insensitive (brown) neurons in the CeA shows a pattern of sensitivity in the medial CeA. Data are means ± SEM, symbols indicate significance by Sidak’s post hoc test, p < 0.05, ∗ between subjects, # within subjects.