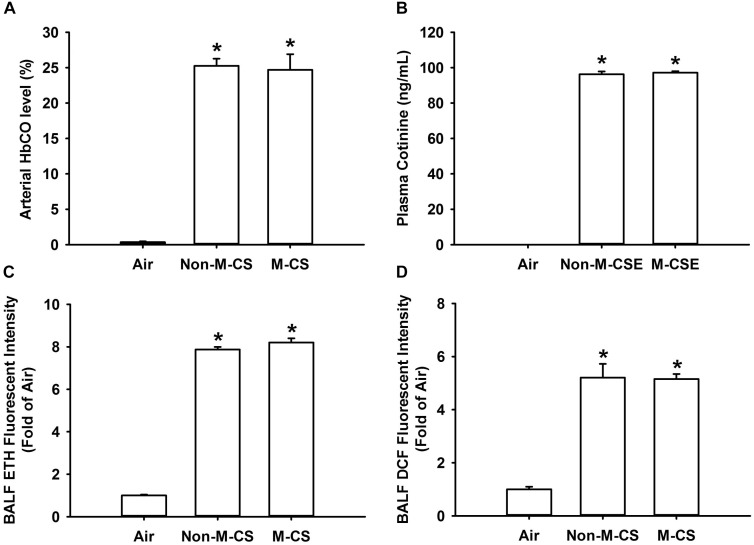
FIGURE 7.
Menthol cigarette smoke and Non-M-CS induce similar levels of biomarkers of CS exposure in mice with acute exposure. Mice were acutely exposed to air, Non-M-CS, or M-CS for 20 min. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and blood samples were collected and analyzed immediately after air or CS exposure. (A) Arterial carboxyhemoglobin (HbCO) concentrations were analyzed by blood gas system. (B) Nicotine concentrations in the blood were assessed with an ELISA kit to detect the levels of cotinine, the predominant metabolite of nicotine. The levels of reactive oxygen species, particularly hydrogen peroxide and superoxide, were measured by DCFH-DA (C) or HE/ETH (D) fluorescent probe assay, respectively. ∗p < 0.05 vs. the air-exposure group. Data in each group are mean ± SEM from six mice. Note that no differences in levels of these biomarkers were detected between the M-CS and Non-M-CS groups.