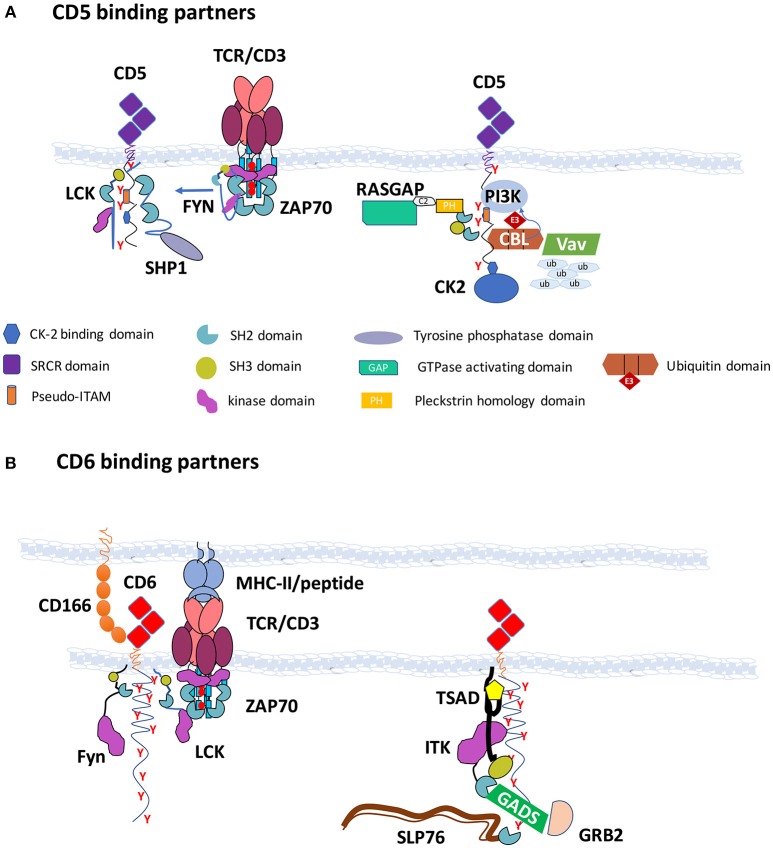
Figure 1.
CD5 and CD6 are hubs for the assembly of effector enzymes and adaptors—(A) CD5 binding partners: CD5 contains in its cytoplasmic tail four tyrosine residues, of which three (Y453, Y465, and Y487) are believed to be phosphorylated upon TCR triggering and can bind the SH2 domains of LCK, RASGAP, CBL, CBLB, SHP1, and PI3K. Recruitment of CBL to the C-terminal region of CD5 is important for the ubiquitylation and degradation of several substrates following TCR engagement, including VAV. CK2 is also able to bind to the cytoplasmic tail of CD5 through other mechanisms. The interaction with FYN is also not dependent on tyrosine phosphorylation. CSK associates with the CD5 signalosome possibly through the cooperation with PAG, CBL, or CBLB. CD5 is represented in duplicate to accommodate all binding partners; (B) CD6 binding partners: CD6 contains in its cytoplasmic tail nine tyrosine residues that when phosphorylated can dock the SH2 domains of SLP76, TSAD, GADS, GRB2, and SHP1. The interactions with LCK, FYN, ZAP70, and ITK were not shown to be dependent on SH2 domain binding to phosphotyrosine residues, but ITK may be recruited through its association with TSAD. CD6 binds through the C-terminal sequence to the PDZ domains of syntenin. The CD6 signalosome is depicted in the right. Structures are not drawn to scale.