Figure 2.
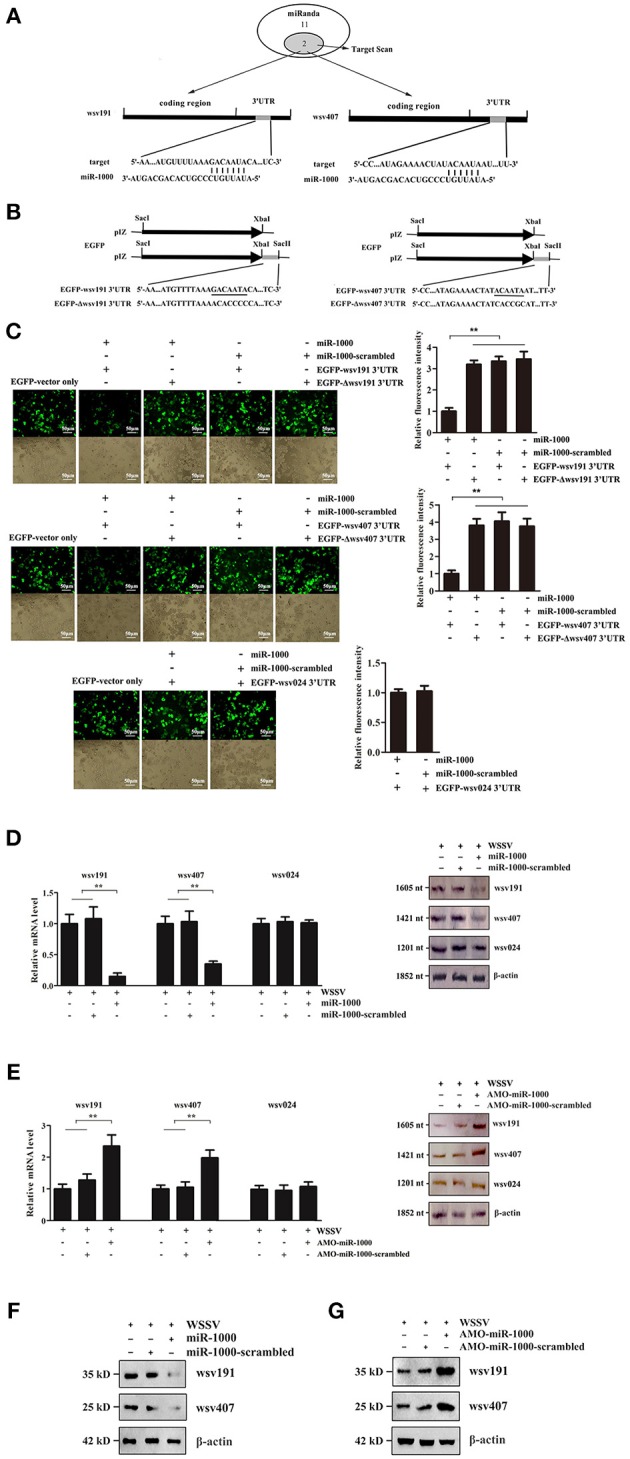
Interaction between host miR-1000 and its target viral genes. (A) Prediction of WSSV genes targeted by miR-1000. Numbers indicated the number of potential genes predicted by the algorithms. (B) Construction of the wild-type and mutated 3′UTRs of wsv191 and wsv407 genes. The sequences targeted by miR-1000 were underlined. (C) Direct interactions of miR-1000 with wsv191 and wsv407 genes in insect cells. High Five cells were co-transfected with miR-1000 and different plasmids. As controls, miR-1000-scrambled, EGFP-Δwsv191-3′UTR and EGFP-Δwsv407-3′UTR were included in the transfection. The interaction between miR-1000 and wsv024, a non-target gene of miR-1000, was also evaluated. At 48 h after co-transfection, the fluorescence intensities of the cells were examined (up). The numbers of cells were indicated with bright-field microscopy (down). Scale bar, 50 μm. (D) Influence of miR-1000 overexpression on the wsv191 or wsv407 mRNA level in vivo. MiR-1000 or miR-1000-scrambled was injected into WSSV-infected shrimp for 48 h, then the level of wsv191 and wsv407 mRNA was determined using quantitative real-time PCR (up) and Northern blot analysis (down). WSSV alone was used as a control. (E) Effects of miR-1000 silencing on the wsv191 and wsv407 mRNA level in vivo. At 48 h after treatment, the level of wsv191, wsv407, and wsv024 mRNA in shrimp was determined using quantitative real-time PCR (up) and Northern blot analysis (down). (F) Impact of miR-1000 overexpression on the wsv191 and wsv407 protein level in vivo. Western blot analysis was carried out to evaluate the viral wsv191 and wsv407 protein levels. β-actin was used as a control. (G) Effects of miR-1000 silencing on the wsv191 and wsv407 protein levels in vivo. Data represented three independent experiments (**p < 0.01).
