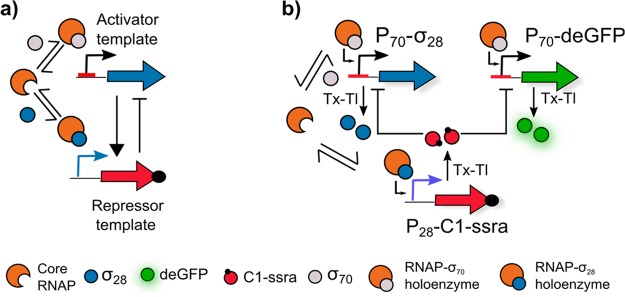
Figure 1.
(a) The oscillator has an activator–repressor motif with the σ28 and C1 serving as activator and repressor, respectively. Critical to the functioning of the oscillator is the competitive binding between the two sigma factors to the core RNAP to form their respective holoenzymes. (b) Schematic representation of the σ28-oscillator. The network topology comprises three DNA constructs: P70-σ28, P28-C1-ssra, and P70-deGFP. The σ70 binds to the RNAP to form the RNAP-σ70 holoenzyme, which binds to the P70 promoter and initiates the expression of σ28 and deGFP. σ28 competitively binds to RNAP to form the RNAP-σ28 holoenzyme, which binds to the P28 promoter and initiates the expression of C1-ssra. C1-ssra exclusively binds to the P70 promoter and represses the production of σ28 and deGFP.