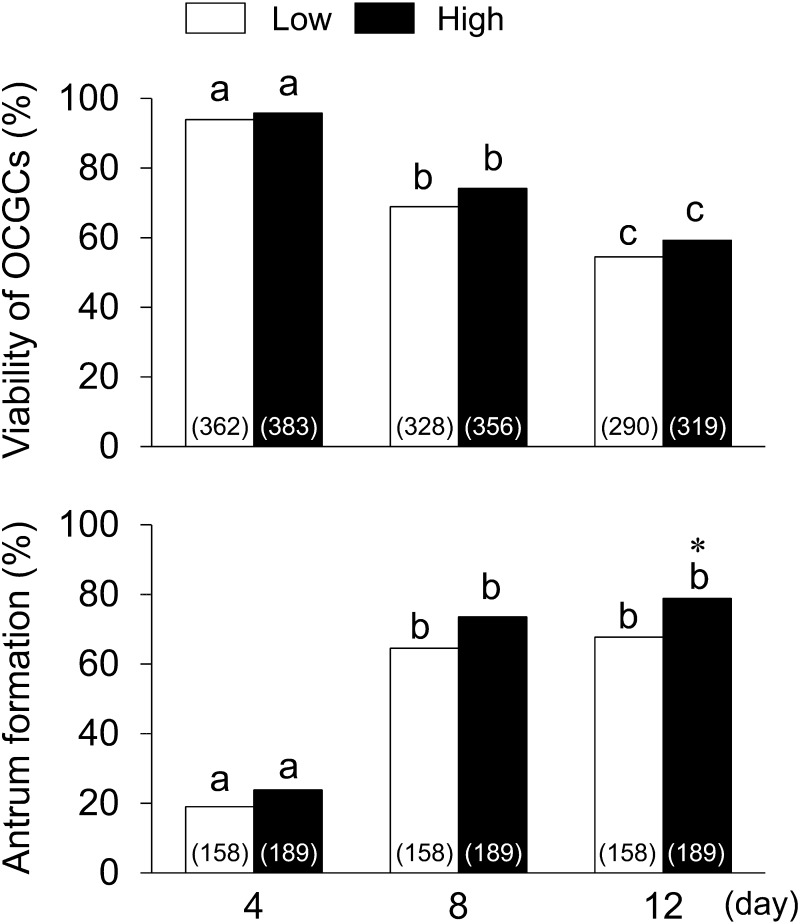
Fig. 4.
Relationships between AFC, viability, and antrum formation in granulosa cell layers of OCGCs. Numbers in parentheses indicate the number of OCGCs; namely, the number of OCGCs in which viability was evaluated on day 12 is a summary of OCGCs cultured for the evaluation of nuclear maturation (low AFC: 193, high AFC: 225) and developmental competence (low AFC: 44, high AFC: 44) in Table 1, and granulosa cell characteristics on day 12 (low AFC: 53, high AFC: 50) in Table 2. The number of OCGCs in which viability was evaluated on day 8 was a summary of OCGCs evaluated as surviving on day 12 and OCGCs evaluated granulosa cell characteristics on day 8 (low AFC: 38, high AFC: 37) in Table 2. The number of OCGCs in which viability was evaluated on day 4 (low AFC: 362, high AFC: 383) was the summary of OCGCs evaluated as surviving at day 8 and OCGCs evaluated granulosa cell characteristics on day 4 (low AFC: 34, high AFC: 27) in Table 2. As shown in Tables 1 and 2, the number of OCGCs in which antrum formation was evaluated (low AFC: 158, high AFC: 189) was the sum of those surviving on day 12 that were used for the evaluation of nuclear maturation (low AFC: 111, high AFC: 137), developmental competence (low AFC: 22, high AFC: 24), and granulosa cell characteristics on day 12 (low AFC: 25, high AFC: 28). a–c Different letters indicate significant differences between different culture periods in the same group (P < 0.05). * An asterisk indicates a significant difference between the low and high AFC groups on the same day (P < 0.05).