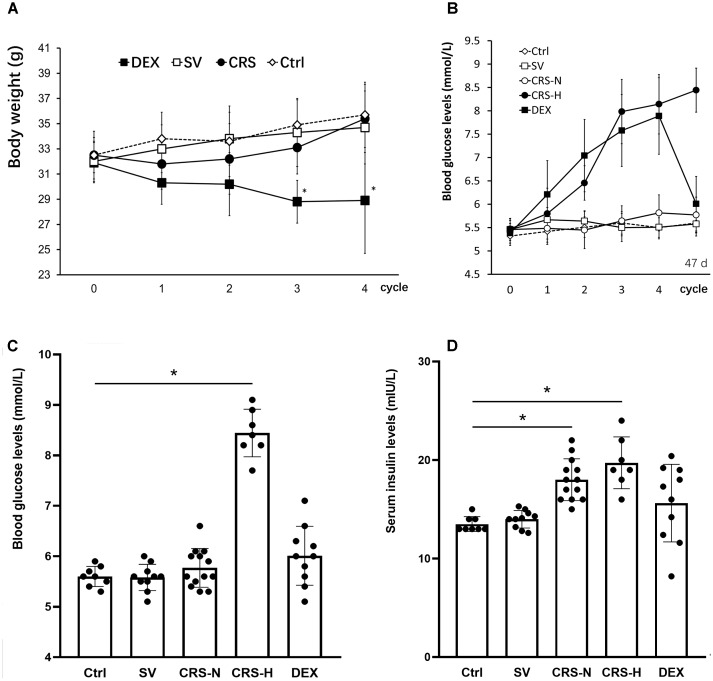
FIGURE 2.
Comparison of body weight changes, fasting blood glucose and serum insulin levels. (A) The effect of restraint on weight gain is transient, while DEX significantly reduces body weight in mice. (B) From the 3rd cycle of CRS, fasting blood glucose levels differentiated, and fasting blood glucose levels in 7 of the 20 mice increased significantly and remained high thereafter. Fasting blood glucose in DEX-administered mice showed a trend of increasing gradually. The fasting blood glucose levels in (B) were detected at the end of each restraint cycle. (C) Fasting blood glucose levels on the 7th day after the end of the 4th cycle. At this time, fasting blood glucose in 7 CRS-hyperglycemia mice was significantly higher than that in the non-restraint control, and there was no significant difference in blood glucose levels in the other groups. (D) Fasting serum insulin levels on the 7th day after the end of the 4th cycle. Serum insulin levels in CRS mice are significantly higher than those of controls regardless of hyperglycemia. The individual differences in serum insulin levels in DEX injected mice were large, and overall there was no significant difference from mice injected with solvent. Ctrl, normal control; SV, solvent injection; CRS-N, CRS-normoglycemia; CRS-H, CRS-hyperglycemia. Data in (A,B) were shown as means ± SEM; ∗p < 0.01.