Figure 6.
LUC7 Proteins Have a Pronounced Effect on Terminal Intron Splicing.
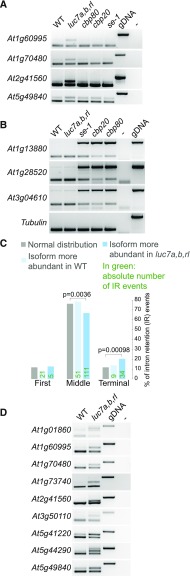
(A) RT-PCR analysis of LUC7-dependent introns in the wild type, luc7 triple mutant, and cbp80, cbp20, and se-1 mutants. RT-PCR analyses were performed using oligonucleotides flanking the LUC7-dependent splicing event.
(B) RT-PCR analysis of CBC/SE-dependent introns in the wild type, luc7 triple mutant, and cbp80, cbp20, and se-1 mutants. RT-PCR analyses were performed using oligonucleotides flanking the CBC/SE-dependent splicing event.
(C) Classification of intron retention according to the intron position (first, middle, or terminal). Only genes with three or more introns were considered for this analysis. A Fisher’s exact test was performed for the statistical analysis (Supplemental File 1).
(D) RT-PCR analysis of genes carrying retained terminal introns in the wild type and luc7 triple mutants. RT-PCR analyses were performed using oligonucleotides flanking the LUC7-dependent splicing event.