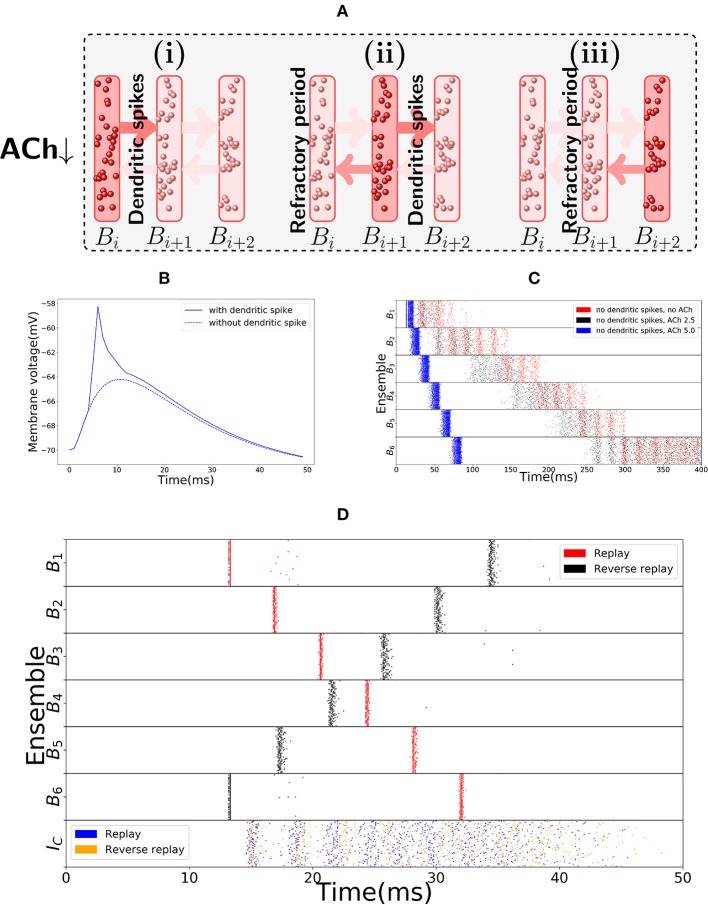
Figure 3.
Replay mode of the sequence encoding module. (A) Synfire chain like synchronous activation of three consecutive bistable units B1, B2, B3. Synchrony triggers dendritic spikes in the next bistable unit, which in turn synchronously activate it. Activity moves in a single direction due to neurons entering a refractory period. (B) Nonlinear effect of a dendritic spike on the membrane potential at the soma of a neuron. There is a latency between the moment the dendrite triggers the dendritic spike and its effect on the soma. All dendritic spikes produce the same stereotypical current pulse effect in the soma. (C) Raster plot of the sequence encoding module in the replay mode, without any dendritic spikes, and showing different levels of cholinergic effect (for ACh factor of 5, only the first five spikes are shown). Without any cholinergic modulation (red), or with the cholinergic factor used in the rest of the paper (black), the sequence encoding module does produce a replay of the path, but on a much slower timescale. Each transition, in the same way as during encoding, takes between 50 and 100 ms. If one increases the cholinergic effect beyond what is reported in Hasselmo and Schnell (1994) and Hasselmo et al. (1995), then as shown in the plot (blue), the transitions between consecutive ensembles is around 15 ms in the upper range of what is often reported in the literature (Lee and Wilson, 2002; Diba and Buzsáki, 2007). We emphasize that only the first five spikes are shown in the blue plot. Due to the fivefold increase in excitatory weights and no counterbalance by inhibition, the network becomes too excitable and the neurons spike at very high rates. Still, the blue plot indicates that it would be possible to produce fast replays if the cholinergic effect would be two times or more of what has been reported in the literature, even without using dendritic spikes. On the other hand, reverse replays rely crucially on dendritic spikes and cholinergic modulatory effect and do not happen without either. (D) Raster plot of the sequence encoding module in the replay mode, now with dendritic spikes. Dendritic spikes increase the speed of replays by two orders of magnitude, making it in line with what is observed during sharp-wave ripples.