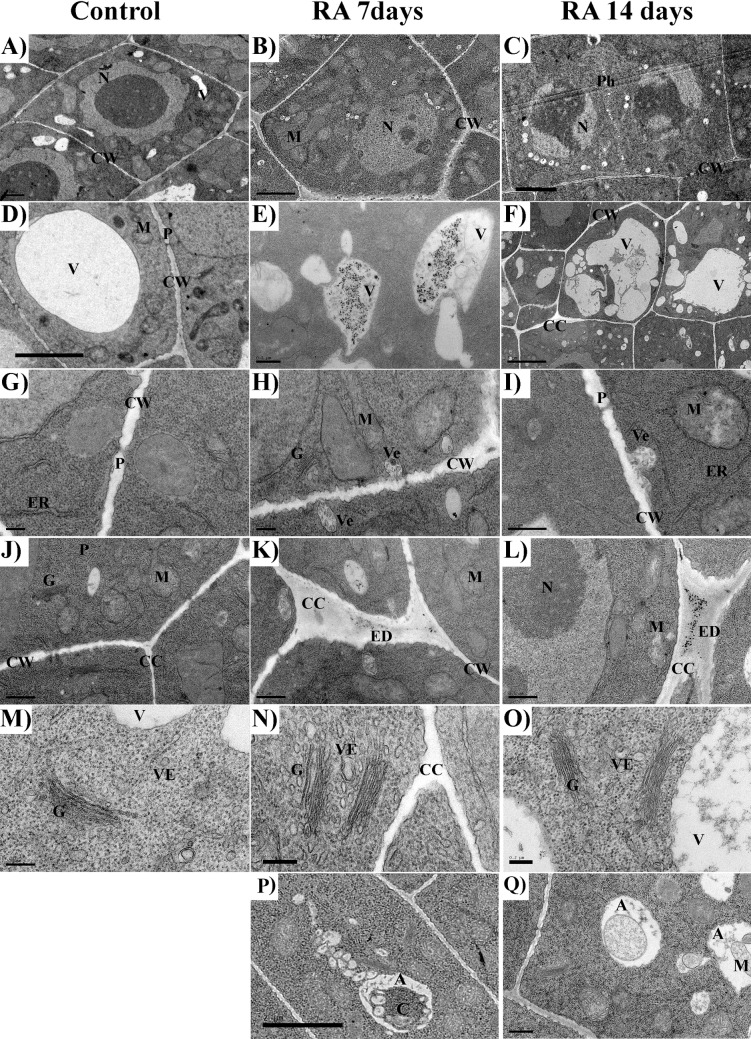
Fig 2. TEM images of rosmarinic acid-treated and untreated Arabidopsis meristems.
TEM images of the apical meristem of control (A, D, G, J, M), and 7 (B, E, H, K, N) and 14 days (C, F, I, L, O) RA-treated (175 μM) Arabidopsis roots: A) control cell of the stele, it should be noted the smooth contour of the nuclei; B) 7 days treated cell of the stele, it should be noted the wavy contour of the nucleus; C) 14 days treated cell of the stele, it should be noted the irregular shape of the nuclei and the presence of fragmented chromatin; D) small vacuole from untreated cell, it should be noted the smooth tonoplast and few fibrillary content; E) small vacuole from 7 days treated cell, it should be noted the presence of a blurry tonoplast and a central accumulation of electrodense material and fine granular material throughout the vacuole volume; F) huge vacuole from 14 days treated cell, it should be noted the classical lytic shape of the vacuole ant the irregular membrane-bound structures containing dense granulose material; G) cell wall of untreated cell with plasmodesmata; H,I) cell walls from 7 and 14 days treated cell with accumulation of electron dense droplets and numerous vesicles in the plasma membrane/cell wall interspace; J) cell corner from untreated cell; K,L) swollen cell corners from 7 and 14 days treated cells with accumulation of electron dense deposits; M) Golgi apparatus from untreated cell; N,O) Golgi apparatus from 7 and 14 days treated cells; should be noted the high production of vesicles; P) single membrane autophagosome in 7 days treated roots, Q) double membrane autophagosome in 14 days treated roots. Nucleus (N), vacuole (V), cell wall (CW), mitochondria (M), phragmoplast (Ph), electrodense deposits (ED), cell corner (CC), plasmodesmata (P), endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi apparatus (G), vesicles (Ve), tonoplast (T), autophagosome (A), cytoplasm (C), mitochondria (M).