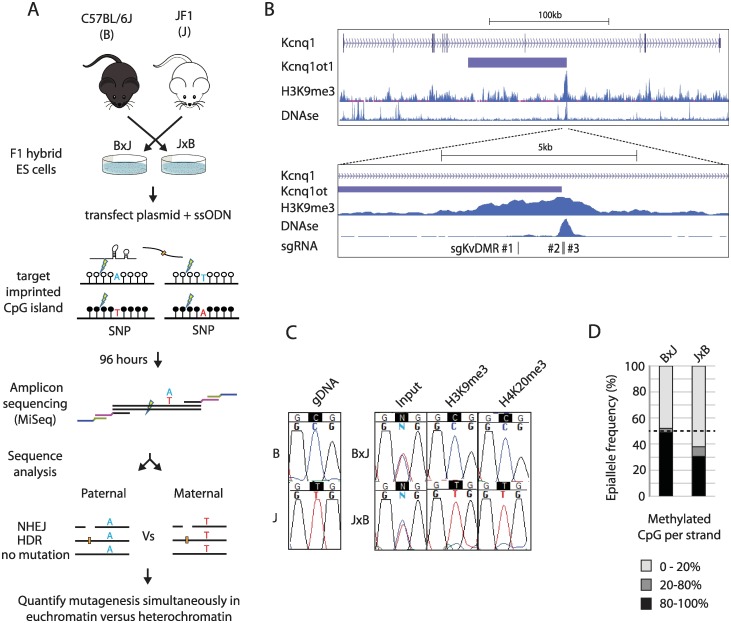
Fig 1. Imprinted chromatin as a model system to quantify epigenetic influences on genome editing.
(A) Schematic outlining the experimental workflow. Throughout the text, F1 hybrid cell lines are depicted with the maternal strain denoted before the paternal strain (i.e., In B×J: B is maternal and J paternal). sgRNAs are designed to cleave approximately 40–100 bp from a heterozygous SNP within imprinted chromatin (open and closed circles). MiSeq amplicons span both the SNP and site of mutation, which allows simultaneous assessment of genome editing outcome and parental allele at high-throughput. (B) Top: schematic showing the imprinted mouse Kcnq1 gene including H3K9me3 ChIP and DNase-I–seq data from mESCs available through EncODE (ENCSR000CFZ, GSM1014187) (bottom). Higher-resolution view of the KvDMR imprinted CpG island within Kcnq1, showing the position of three sgRNAs used in panel E. (C) Allele-specific enrichment of H3K9me3 and H4K20me3. PCR fragments spanning the target sites of sgKvDMR#2 and #3 were amplified from input, or ChIP DNA prior to Sanger sequencing across an allelic SNP. gDNA = genomic DNA from purebred mice. (D) Example of CpG methylation data from the KvDMR locus. Bisulphite-converted gDNA was subjected to Illumina amplicon sequencing across a region spanning 13 CpG dinucleotides (S1A Fig), and reads were classified according to the proportion of nonconverted (methylated) CpGs. The black dashed line indicates the expected level of methylation across all alleles when imprinting is completely maintained (50%). In subsequent editing experiments, the percentage of hypermethylated (>80%) strands is reported together with histograms showing allele-specific mutation frequency. Quantitative data underlying panel D are provided in S1 Data, and details of MiSeq libraries including SRA accessions are provided in S2 Data. ChIP, chromatin immunoprecipitation; gDNA, genomic DNA; HDR, homology-directed repair; mESC, mouse embryonic stem cell, NHEJ, nonhomologous end joining; sgRNA, single guide RNA; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism; SRA, Sequence Read Archive; ssODN, single-stranded oligodeoxynucleotide.