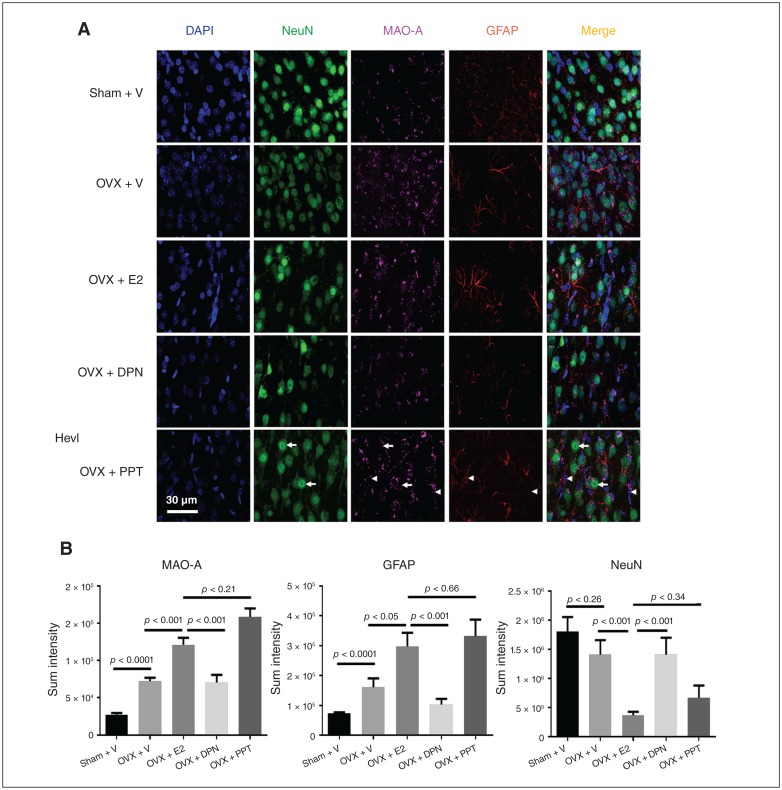
Fig. 6.
E2 and ERα-specific agonist increased MAO-A and GFAP expression, and reduced NeuN expression in the dorsal raphe of OVX rats. ERβ-specific agonist ameliorated GFAP expression and maintained NeuN expression in the dorsal raphe of OVX rats (180 d post-OVX). (A) Representative immunofluorescence images of the dorsal raphe of OVX female rats treated with vehicle (sham + vehicle), OVX + vehicle, OVX + E2, OVX + DPN and OVX + PPT. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Note the nuclear staining of NeuN (green), cytosol punctate staining of MAO-A (magenta) and glial cell–specific staining of GFAP (red). Scale bar = 50 μm. Arrows and arrowheads indicate the representative cells expressing MAO-A + NeuN and MAO-A + GFAP, respectively. (B) We analyzed the immunoreactive intensities of MAO-A, GFAP and NeuN in the dorsal raphe of rats using 1-way ANOVA and a subsequent Bonferroni post hoc test. Note the significant increases of MAO-A (F4,5248 = 33.66, p < 0.001) and GFAP (F4,19808 = 11.88, p < 0.001) expression in OVX rats; however, OVX did not alter the expression of NeuN (F4,6953 = 4.95, p = 0.26). Both E2 and PPT increased MAO-A and GFAP (p < 0.001 and p < 0.05, respectively, for E2; p < 0.001 and p < 0.05, respectively, for PPT) v. OVX, but reduced NeuN expression (p < 0.001 for E2 and p < 0.06 for PPT); DPN ameliorated MAO-A and GFAP expression (p = 0.86 for MAO-A and p = 0.09 for GFAP) and maintained NeuN expression (p = 0.9) in rats 180 d after OVX. ANOVA = analysis of variance; DPN = diarylpropionitrile; E2 = estradiol; MAO-A = monoamine oxidase A; OVX = ovariectomy; PPT = propylpyrazoletriol.