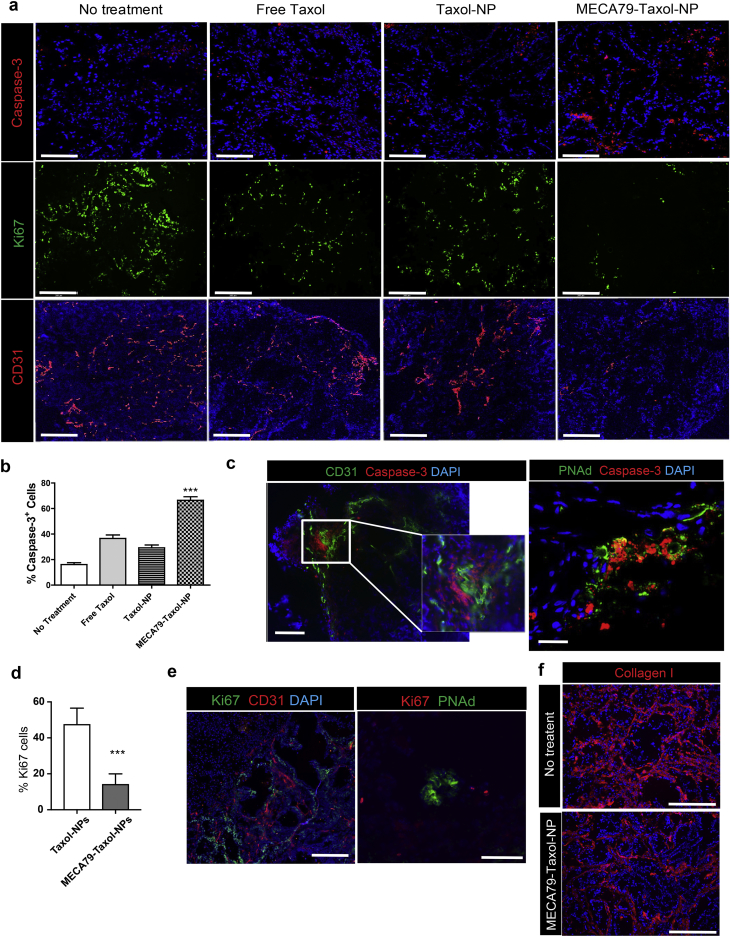
Fig. 5.
Histological analysis of PDAC following treatment with MECA79-Taxol-NPs. (a) Immunofluorescence staining of the tumor at the end of the study demonstrated that treatment with MECA79-Taxol-NPs resulted in higher apoptosis (caspase-3+) of cancer cells, lower cellular proliferation (Ki67+), and decreased vascularization (CD31+) (Scale bar = 200 μm). (b) Quantification of the caspase-3+ cells using ImageJ software (***p < 0.001, ANOVA, n = 3 mice/group). The data are presented as the mean and SEM. (c) Representative immunofluorescence images of the PDAC tumor for markers of vasculature (CD31 and PNAd in green) and apoptosis (caspase-3 in red) following treatment with MECA79-Taxol-NPs (Scale bar = 200 μm). (d) Quantification of the Ki67+ cells using ImageJ software (***p < 0.001, student's t-test, n = 3 mice/group). The data are presented as the mean and SEM. (e) Representative immunofluorescence images of the PDAC tumor for markers of vasculature (CD31 and PNAd) and proliferation (Ki67) in the no-treatment group (Scale bar = 200 μm for CD31, 100 μm for PNAd). (f) Immunofluorescence staining for collagen I (red) of the PDAC tumor comparing the groups that received no treatment and MECA79-Taxol-NP (Scale bar = 100 μm).