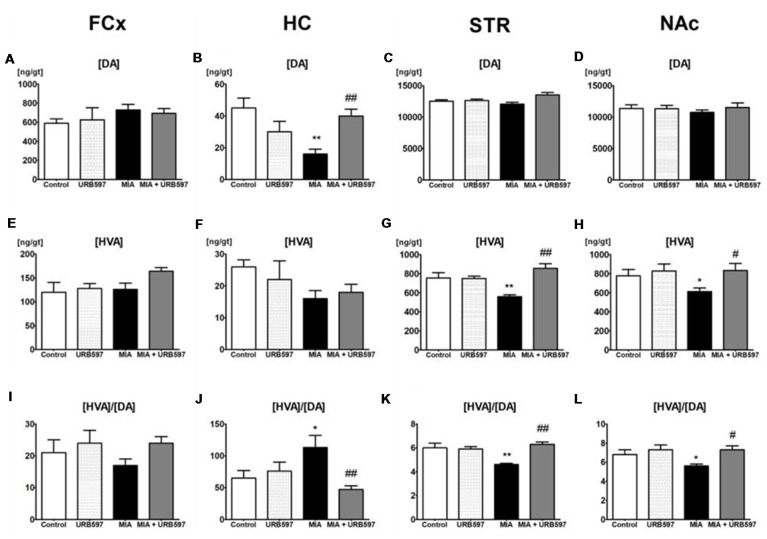
Figure 1.
The effect of URB597 on osteoarthritis (OA)-produced decreases in dopaminergic neurotransmission in the investigated brain structures; (A,E,I) frontal cortex (FCx), (B,F,J) hippocampus (HC), (C,G,K) striatum (STR) and (D,H,L) nucleus accumbens (NAc). Samples were collected 28 days after OA induction, 1 h after i.p. administration of URB597 or vehicle. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM and represent normalized averages derived from 6 to 10 samples for each group. The results were analyzed by means of one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by Duncan’s post hoc tests. Statistical significance: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. Control group; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs. OA group. One-way ANOVA indicated a significant effect of OA on the rate of dopamine (DA) metabolism in STR (F(3,22) = 13.89; P < 0.00002) and NAc (F(3,21) = 4.18; P < 0.01); DA concentration in STR (F(3,22) = 4.32; P < 0.01) and HC (F(3,22) = 6.96; P < 0.001) and homovanillic acid (HVA) concentration in STR (F(3,22) = 13.10; P < 0.00004) and NAc (F(3,21) = 3.48; P < 0.03).