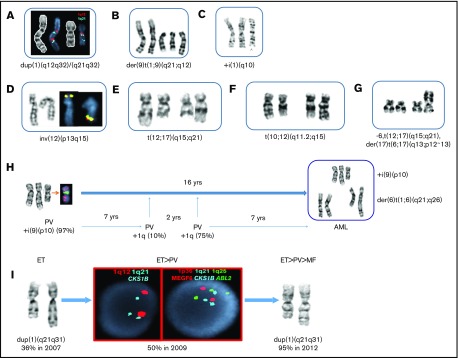
Figure 1.
Structural chromosomal abnormalities involving chromosomes 1, 12, and 17 in patients with MPN and progression of disease. (A-G) Partial karyotypes showing gains of 1q and 12q structural rearrangements. The most frequent unbalanced translocations identified were +der(9)t(1;9)(q21;q12), resulting in 3 copies of 1q and 3 copies of 9p. Extra copies of 1q were also observed as the whole-arm or part of the +1q participated in unbalanced translocations to chromosomes 1, 13, 14, 15, 18, 19, 21, or 22 (26 patients). (A) Two different 1q duplications were inserted in dup(1q) in a patient with MF. The first region involved 1q12-q32, and the second region involved 1q21-32, showing both duplication of q12 (red) and q21 (aqua). (B) A partial karyotype from a patient with PV showing the most frequent gain of 1q, der(9)t(1;9)(q21;q12), resulting in 3 copies of 9p and JAK2. (C) A partial karyotype showing isochromosome 1q in a patient with MF, resulting in 4 copies of 1q and MDM4. (D) The most frequent 12q abnormalities are inversions of chromosome 12. In this partial karyotype, as a result of pericentric inversion, ETV6 (yellow), normally residing on the short arms (12p13.2), has been relocated to 12q15, where MDM2 is localized. (E) The second most common 12q rearrangements were balanced translocations between 12q and the following partner chromosomes: 2, 5, 8, and 10. A partial karyotype showing a balanced t(12;17)(q15;q21) translocation involving the breakpoint at 12q15, as does the t(10;12) (see panel F) observed in 3 patients with MF, is shown here. (F) A partial karyotype showing a balanced translocation t(10;12)(q11.2;q15) in a patient with MF. Two patients with MF were identified with the identical translocation. (G) A different type of t(12;17) translocation identified in a patient who progressed to MPN-AP/BP. The patient had a complex karyotype, and this partial karyotype shows both the 12q15 and the 17p13, where TP53 resides, were rearranged in the same clone. (H) Sequential cytogenetic studies spanning 16 years. Initial cytogenetic study (1996) at the time of PV diagnosis revealed a gain of isochromosome 9p, resulting in tetrasomy 9p (and 4 copies of JAK2) in 97% of metaphase cells. An additional 20 cytogenetic studies revealed gain of 1q [der(6)t(1;6)] initially in 10% of i(9p) cells for the first time 7 years after the diagnosis. As the number of cells harboring +1q increased, the patient progressed to MF, and finally to MPN-BP. This progression was also accompanied by jumping 1q, whereby long arms of chromosome 1 were translocated to 4 different recipient chromosomes, leading to the 6 copies of 1q and transformation of the disease to MPN-BP. (I) At the time of ET diagnosis, the patient had 36% of cells with dup(1q). Within 2 years, the patient progressed to PV, which was accompanied by 50% of interphase cells showing gain of CKS1B (aqua) at 1q21 and 3 copies of ABL2 (green) at 1q25, as detected by FISH. The patient progressed to MF 5 years after the diagnosis of ET, at which time 95% of the cells harbored duplication of 1q21-q31 region.