Fig. 4.
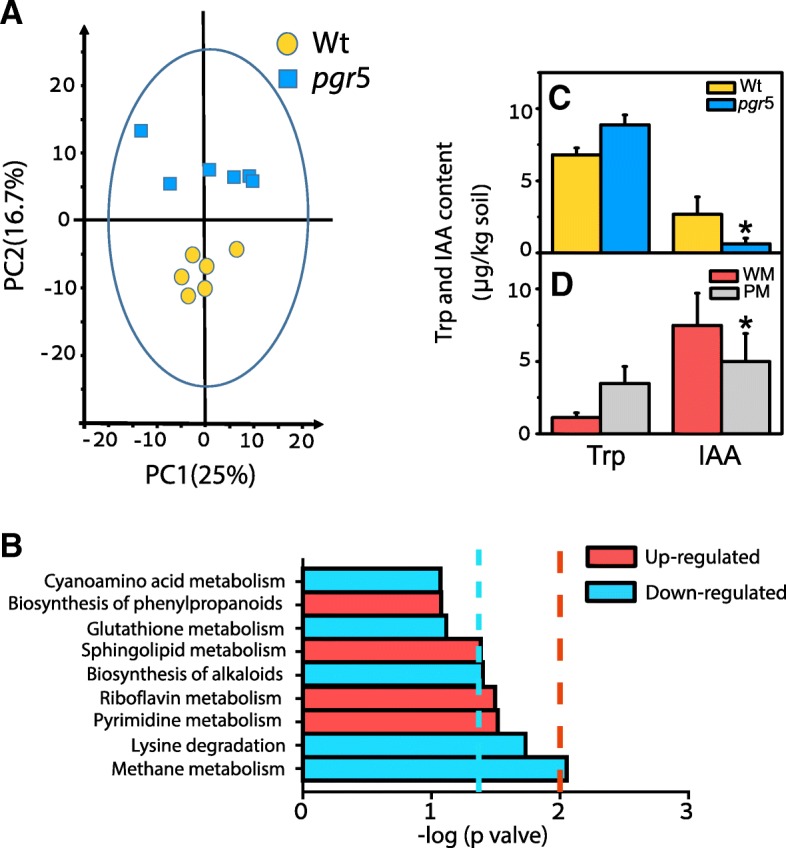
Root exudates of the two Arabidopsis lines. a Principal component analysis (PCA) of root exudates in the Wt and pgr5 treatments (n = 6) grown hydroponically. b Differentially released exudates (p < 0.05) in the Wt and pgr5 treatments were classified into corresponding metabolic pathways inferred from the KEGG pathway database (n = 6). c Tryptophan (Trp) and indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) contents in the soil of the cultures of Wt Arabidopsis or pgr5 mutants grown for three generations in microcosms. d Trp and IAA contents in the soil-cultured Wt Arabidopsis for one generation that had been in advance added the microbiota from the Wt (WM) or the pgr5 mutant (PM) Arabidopsis. Red and blue bars indicate that the exudates for a given pathway are mainly up- or downregulated, respectively, in the Wt cultures relative to the pgr5 mutant cultures. The blue and red vertical dashed lines depict p = 0.05 (−log (0.05) = 1.3) and p = 0.01 (−log (0.01) = 2), respectively. Asterisk represents a significant difference (p < 0.05). Values are means ± SDs (n = 6)
