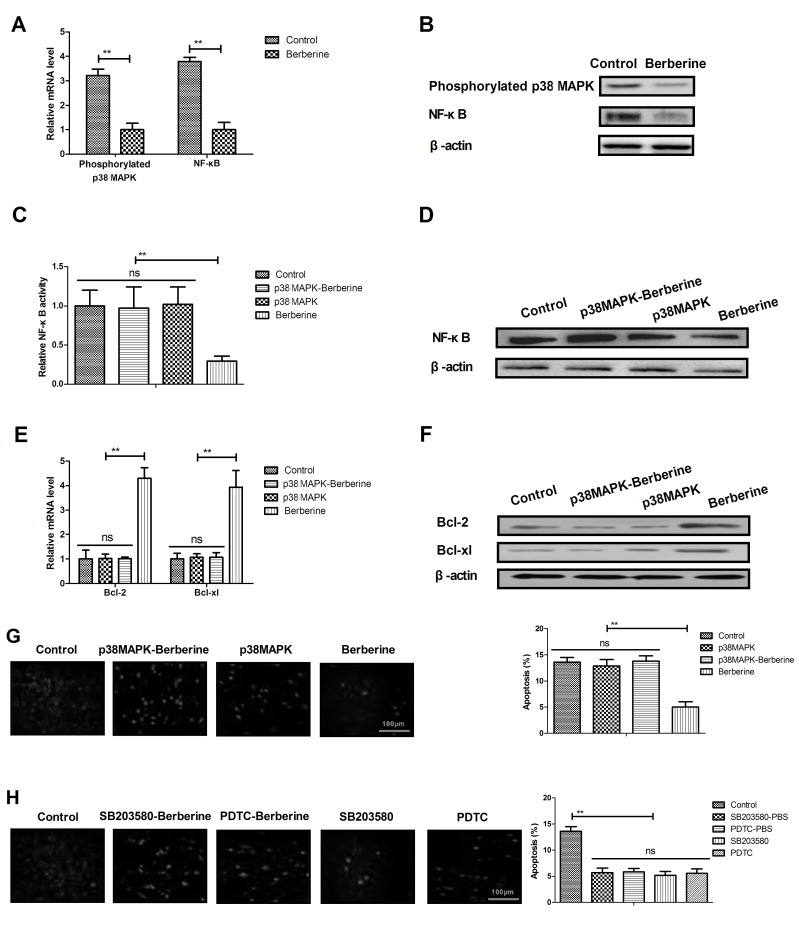
Figure 4.
Berberine treatment improves anoxia-reoxygenation injury via the p38 MAPK-mediated NF-κB signaling pathway. Phosphorylated p38 MAPK and NF-κB (A) mRNA and (B) protein expression in myocardial cells isolated from a mouse model of anoxia-reoxygenation injury. p38 MAPK overexpression ameliorates the berberine-induced upregulation in NF-κB (C) activity and (D) expression in myocardial cells. p38 MAPK overexpression suppresses the berberine-induced overexpression of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xl (E) mRNA and (F) protein in myocardial cells. (G) Effects of p38 MAPK overexpression on Berberine-inhibited myocardial apoptosis of myocardial cells isolated from experimental mice determined by TUNEL. (H) Effects of p38 MAPK or NF-κB inhibitor on the apoptosis of myocardial cells isolated from PBS-treated experimental mice determined by TUNEL. **P<0.01. MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; NF, nuclear factor; Bcl, B-cell lymphoma; xl, extra large.