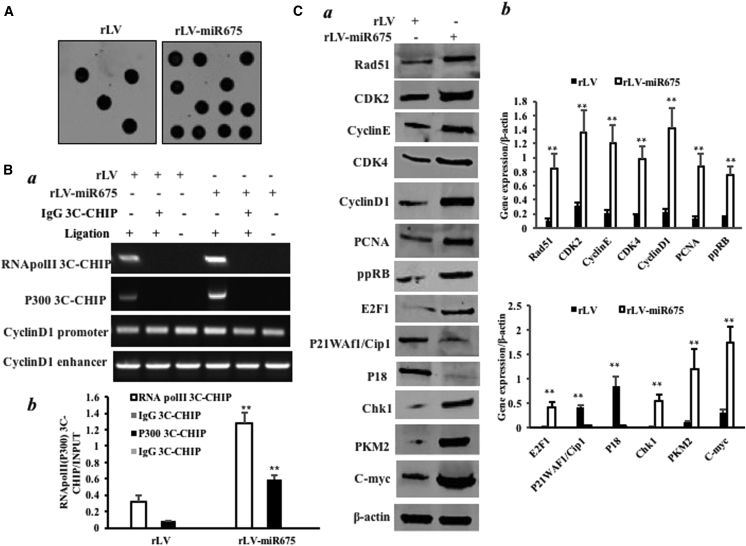
Figure 7.
miR675 Triggers MSI and Abnormal Gene Expression in the Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Infected with rLV and rLV-miR675, Respectively
(A) Microsatellite instability (MSI) analysis through dot blot (slot blot) using various biotin-labeling MSI probes (biotin-MSIs). (B) (a) Chromosome conformation capture (3C)-chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) with anti-P300 and anti-Pol II. The chromatin was cross-linked, digested with restriction enzymes, and ligated under conditions that favor intramolecular ligation. Immediately after ligation, the chromatin was immunoprecipitated using an antibody (anti-P300, anti-Pol II) against the protein of interest. Thereafter, the cross-links were reversed and the DNA was purified further. The PCR anlysis was applied for detecting CyclinD1 promoter-enhancer coupling product using CyclinD1 promoter and enhancer primers. The CyclinD1 promoter and enhancer was the INPUT. (b) The quantitative analysis of ChIP-3C. (C) (a) Western blotting with anti-Rad51, anti-CDK2, anti-CyclinE, anti-CDK4, anti-CyclinD1, anti-PCNA, anti-ppRB, anti-E2F1, anti-P18, anti-P21, anti-PKM2, anti-c-Myc, and anti-Chk1. β-actin was the internal control. (b) The gray scan analysis of positive bands of western blotting.