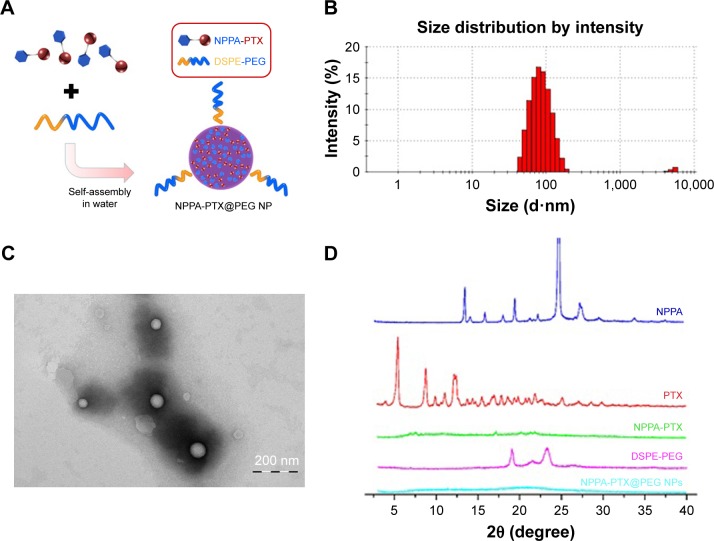
Figure 1.
The preparation and characteristics of NPPA-PTX@PEG NPs.
Notes: (A) The preparation of NPPA-PTX@PEG NPs. NPPA-PTX@PEG NPs was prepared by precipitation. Briefly, both NPPA-PTX and DSPE-PEG (NPPA-PTX:DSPE-PEG =1:0.1, w/w) were dissolved in DMSO and added dropwise to distilled water. NPPA-PTX@PEG NPs occurred spontaneously. (B) A typical particle size and distribution of NPPA-PTX@PEG NPs. The particle size and distribution of NPPA-PTX@PEG NPs were assayed by DLS measurements on a Nano ZS instrument. (C) The TEM image of NPPA-PTX@PEG NPs. TEM was performed using a JEM 1400 microscope operating at 140 kV using a permeable carbon-coated copper grid to examine the morphology of NPPA-PTX@PEG NPs. (D) The X-ray diffraction patterns of NPPA-PTX and NPPA-PTX@PEG NPs. The X-ray diffraction patterns of the samples, including NPPA, PTX, NPPA-PTX, and NPPA-PTX@PEG NPs were all measured using a D/MAX 2000 rotating anode X-ray diffractometer equipped with a Cu-Kα X-ray source (λ=1.541 nm, 40 kV/100 mA).
Abbreviations: DLS, dynamic light scattering; DSPE-PEG, 1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine [methoxy(polyethylene glycol)2000]; NPPA, 3-(2-nitrophenyl) propionic acid; NPPA-PTX@PEG NPs, NPPA-PTX nanoparticles prepared by NPPA-PTX and DSPE-PEG (NPPA-PTX:DSPE-PEG =1:0.1, w/w); NPs, nanoparticles; PTX, paclitaxel; TEM, transmission electron microscopy; XlogP, theoretical partition coefficient.