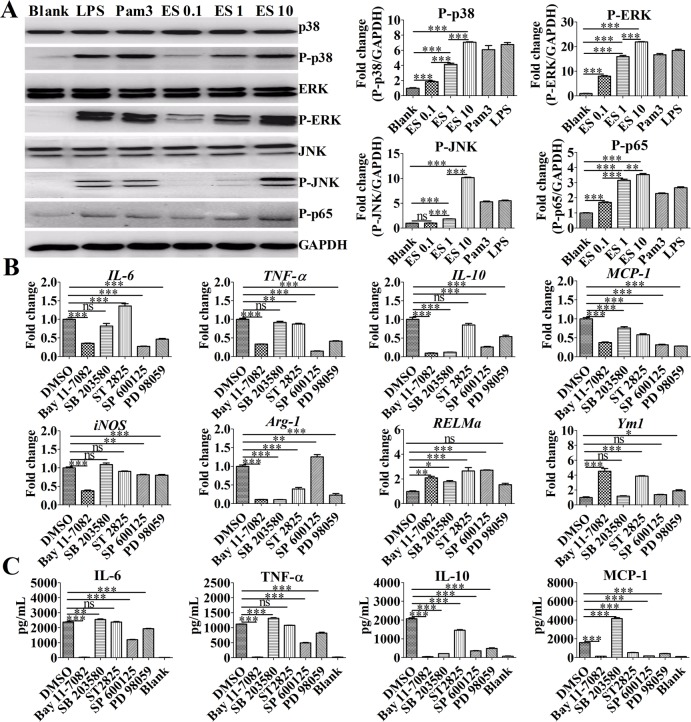
Fig 2. ES promoted M2b polarization and inflammatory cytokine production by activating the MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway.
(A) Immunoblot of P-p38, P-p65, P-ERK1/2, and P-JNK in the lysates of BMDMs after stimulation for 30 min. Graphical representations of band intensities are shown in the right panel. Expression of P-p38, P-p65, P-ERK1/2, and P-JNK was normalized to GAPDH expression. (B) The levels of IL-6, TNF-a, IL-10, MCP-1, Arg-1, RELMa, Ym1, and iNOS mRNA in BMDMs were analyzed by RT-qPCR. An NF-κB inhibitor (BAY 11–7082, 10 μM), p38 MAPK inhibitor (SB 203580, 1 μM), JNK inhibitor (SP 600125, 10 μM), MyD88 homodimerization inhibitor (ST 2825, 10 μM), or ERK inhibitor (PD 98059, 10 μM) was added to different groups of cells and incubated for 1 h before ES antigen treatment for 4 h. (C) Levels of IL-6, MCP-1, TNF-α, and IL-10 in the supernatants of macrophages stimulated with ES (1 μg/mL) were measured by ELISA. An NF-κB inhibitor (BAY 11–7082, 10 μM), p38 MAPK inhibitor (SB 203580, 1 μM), JNK inhibitor (SP 600125, 10 μM), MyD88 homodimerization inhibitor (ST 2825, 10 μM), or ERK inhibitor (PD 98059, 10 μM) was added to the cells and incubated for 1 h before antigen treatment for 24 h. Data are the results from a representative experiment from three independent experiments and are analyzed by one-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ns, not significant.