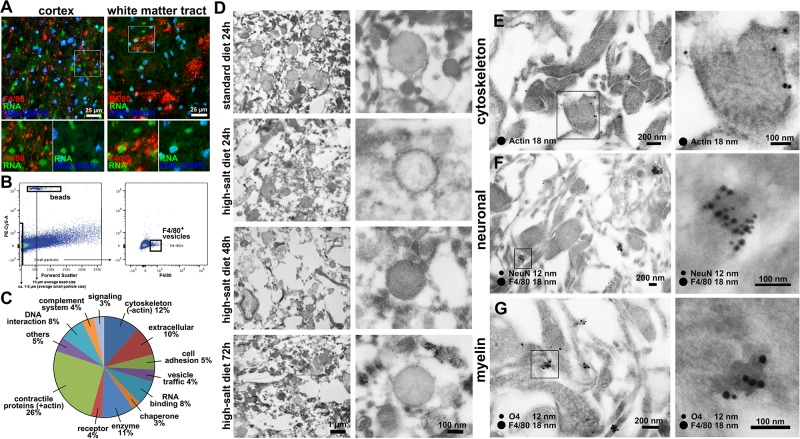
Fig 4. Identification of migrasome components.
(A) Co-staining of F4/80 and RNA did not show RNA-signaling within the migrasome either in cerebral cortex or white matter tracts. (B) Gating strategy: All particles smaller than 2 μm in size compared to the added beads were sorted for F4/80+-signal. Quantification was performed by comparing the number of beads with the number of F4/80-positive particles. Quantification revealed a higher amount of F4/80+-vesicles in high-salt diet group when compared to the standard diet. (C) Proteomic analyses demonstrated that the migrasome was mainly composed of contractile proteins actin and myosin, cytoskeleton and annexin proteins, which were previously described to be involved in trafficking and organization of vesicles [25]. (D) Electron microscopy confirmed the typical morphological characteristics of the migrasome on ultrastructural level. Time course analyses revealed an increasing degree of extracellular tissue damage within the first 72 h after stroke. Vesicle close-ups reveal cup-like structures carrying spherical structures in all investigated time-points and treatments. (E) Immunogold-staining shows actin-postive signals especially in the outer layer of the vesicle-like structures. (F) Co-staining of F4/80 and NeuN confirms fluorescence microscopic observations and shows a distinct clustering of F4/80 and NeuN-signals in small vesicle-like structures. (G) F4/80 and O4-staining also reveals a solid co-localization in node-like structures.