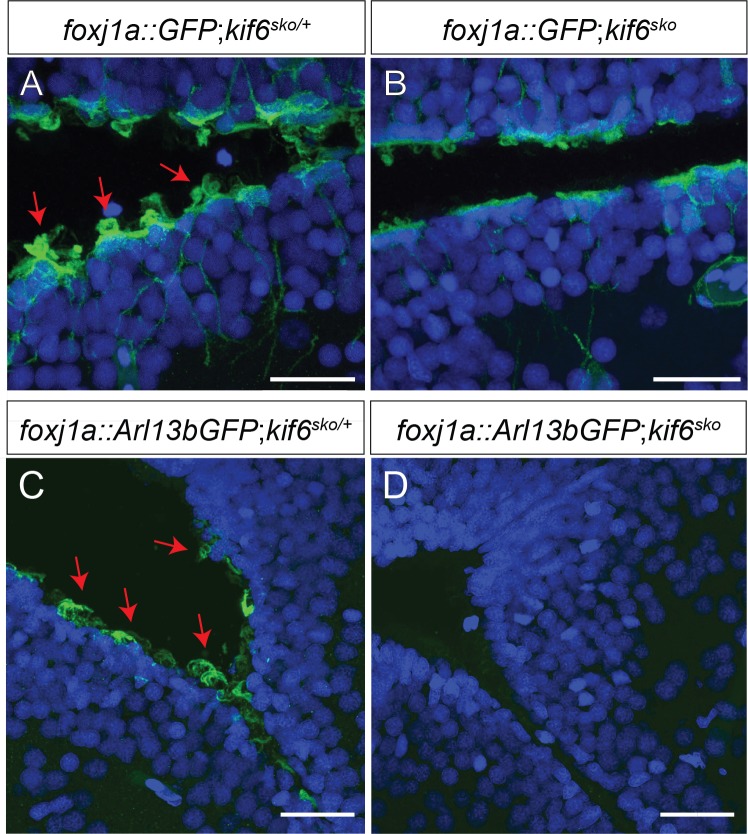
Fig 6. kif6 mutant zebrafish display defects in the formation of the ependymal cell cilia in the brain.
(A-D) Immunofluorescence of Tg[foxj1a::GFP] (A, B) and Tg[foxj1a::Arl13bGFP] transgenic zebrafish in both heterozygous kif6sko/+ (A, C) and homozyogus kif6sko mutant (B, D) zebrafish backgrounds assayed with αGFP (green) and DAPI (nuclei, blue). The Tg[foxj1a::GFP] transgene demonstrates that GFP positive ECs are present in both genotypes. In contrast, kif6sko/+ heterozygous zebrafish display numerous apical tufts of cilia (red arrows; A) projecting into the ventricle lumen, which are markedly reduced in kif6sko mutant zebrafish (B). Similar results were observed with the Tg[foxj1a::Arl13bGFP] transgene, showing a obvious reduction in Arl13b-GFP positive EC axonemes in kif6sko mutant zebrafish (D), which are robustly labeled in kif6sko/+ heterozygous fish (C). Scale Bars: 20μm.