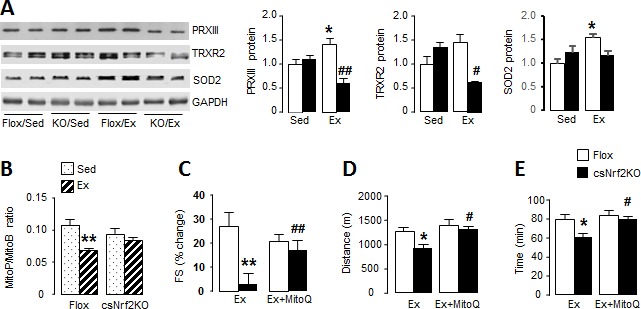
Figure 4. Cardiomyocyte Nrf2 is required for increase in mitochondrial antioxidant capacity with exercise.
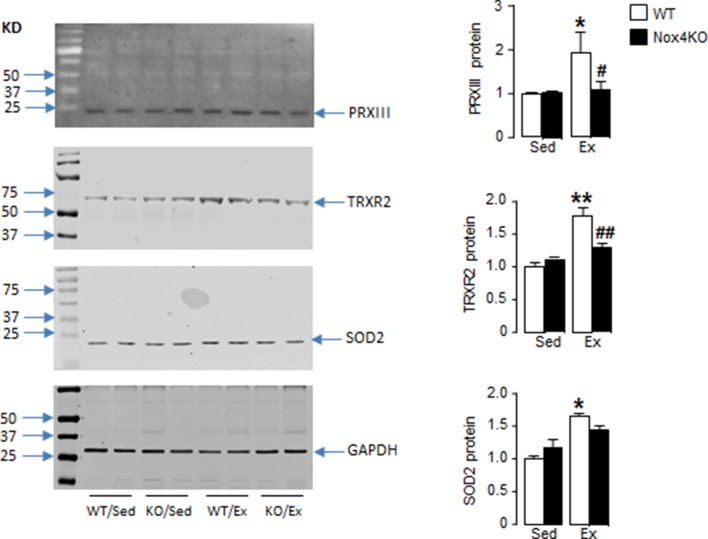
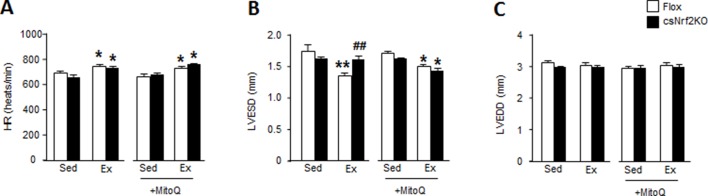
(A) Western blots for peroxiredoxin III (PRXIII), thioredoxin reductase-2 (TRXR2) and superoxide dismutase-2 (SOD2) in heart of csNrf2KO and Flox controls after acute exercise (Ex). Mean data from n = 4–6/group are shown on the right. *p<0.05 vs respective sedentary controls (Sed); #p<0.05, ##p<0.01 vs Flox/Ex, 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post hoc analysis. (B) In vivo mitochondrial H2O2 levels assessed by the MitoP/MitoB ratio in hearts of csNrf2KO mice and controls after acute exercise. **p<0.01 vs Flox/Sed, 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post hoc analysis (n = 5–6/group). (C) MitoQ treatment improved cardiac contractile performance at peak exercise in csNrf2KO mice. n = 6–7/group. (D) and (E) The effect of MitoQ treatment on maximal running distance and time. n = 7–11/group. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 vs Flox/Ex, #p<0.05, ##p<0.01 vs csNrf2KO/Ex, 2-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post hoc analysis.