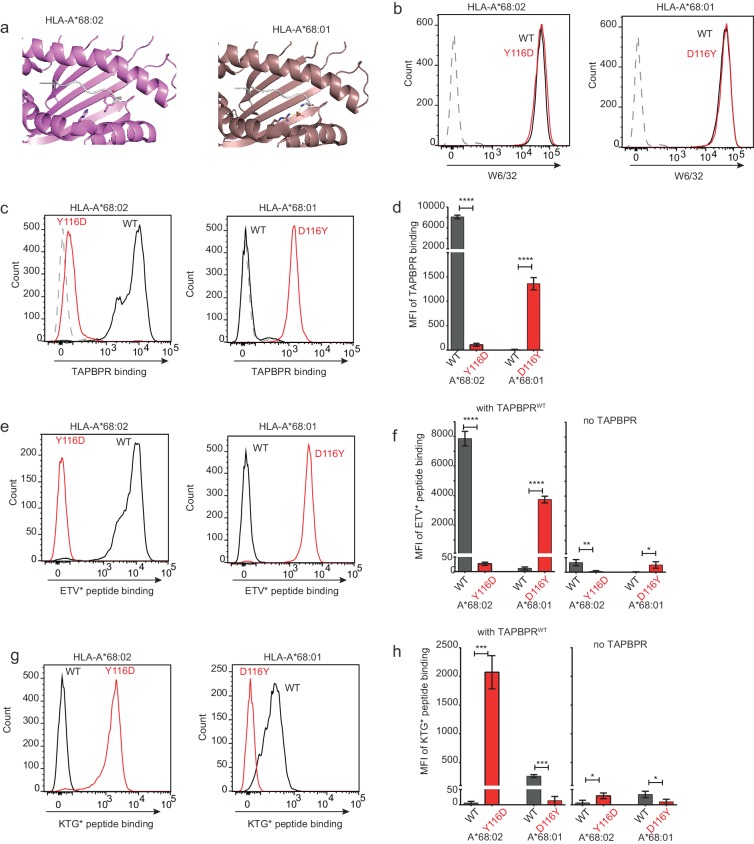
Figure 7. Mutation of the MHC I F pocket alters TAPBPR-mediated peptide editing.
(a) PyMOL images of the binding grooves of HLA-A*68:02 (PDB ID 4HX1) and -A*68:01 (PDB ID 4HWZ), with residues found at position 116 and 114 highlighted. (b) Histograms show the surface expression of HLA-A*68:02WT, -A*68:02Y116D, -A*68:01WT and -A*68:01D116Y, detected using W6/32, when expressed in HeLa-M-HLA-ABCKO cells. (c, e, g) HeLaM-HLA-ABCKO cells expressing the panel of HLA-A*68 molecules were incubated with 1 μM of soluble TAPBPR for 15 min at 37°C, followed by either (c) detection of surface bound TAPBPR using PeTe4, or incubation with (e) 10 nM ETVSK*QSNV (ETV*) or (g) 100 nM KTGGPIYK*R (KTG*) peptide for 15 min and 60 min, respectively. In (c), staining with an isotype control antibody is included as a control (grey dotted line). While histograms in c, e, g are representative images, the bar graphs in d, f, h summarise the MFI of (d) TAPBPR binding and (f and h) fluorescent peptide binding in the presence and absence of TAPBPR, from three independent experiment ± SD. ****p ≤ 0.0001, ***p ≤ 0.001, P** ≤ 0.01, *p ≤ 0.05.
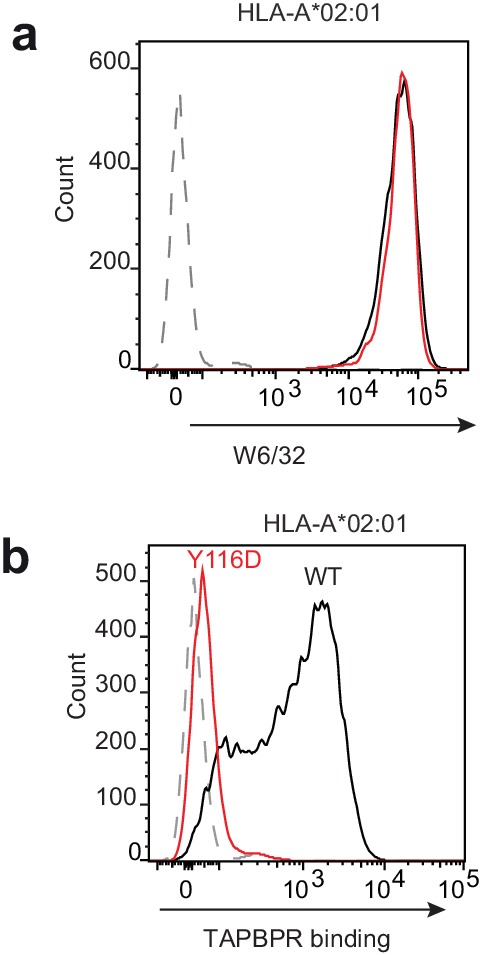
Figure 7—figure supplement 1. Mutation of the HLA-A2 F pocket alters TAPBPR binding.