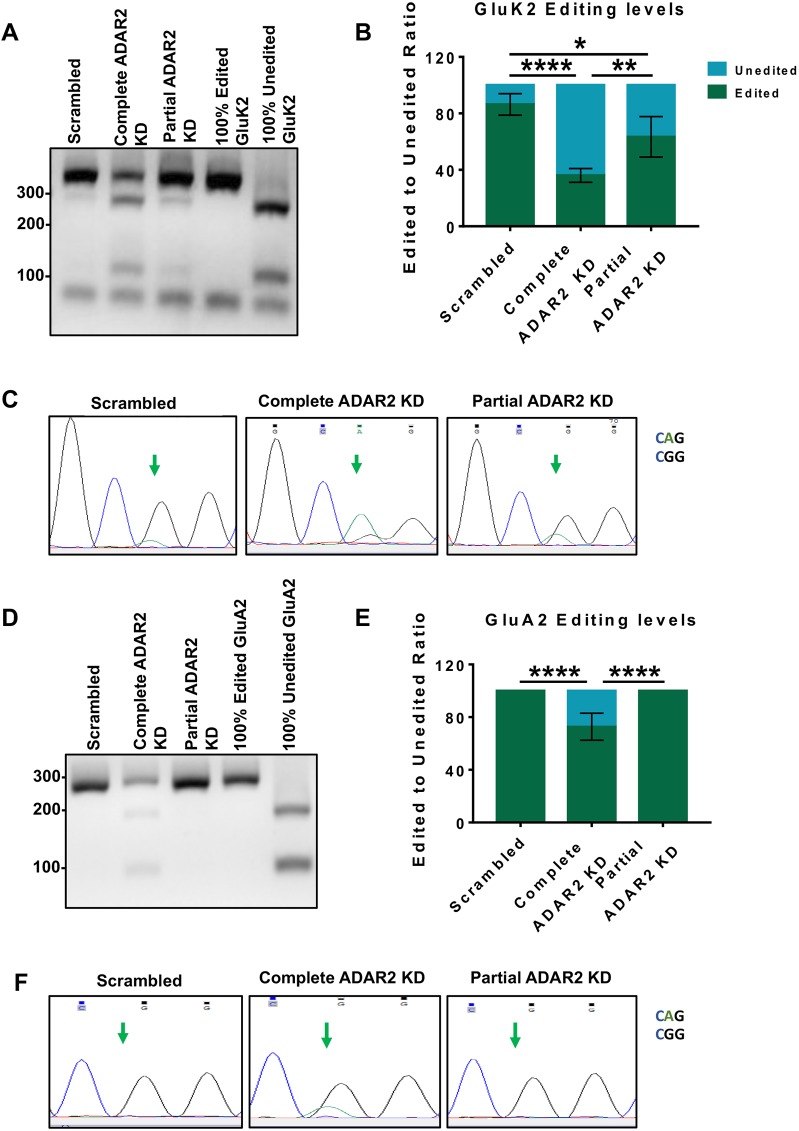
Fig. 2.
Complete and partial ADAR2 knockdown differentially alter GluK2 and GluA2 Q/R editing. (A) RT-PCR and BbvI digestion analysis of GluK2 Q/R editing from hippocampal neurons infected with scrambled, complete or partial shRNAs for ADAR2 knockdown (KD). (B) Quantification of results from A for four independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ****P<0.0001 (one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test). (C) Sanger sequencing chromatographs of the GluK2 PCR products from hippocampal neurons infected with scrambled, complete or partial shRNAs for ADAR2 KD, showing dual A and G peaks at the editing site, indicated by the green arrows. The green peak represents an A (unedited) base read and black represents a G (edited) base read. (D) RT-PCR and BbvI digestion analysis of GluA2 Q/R editing from hippocampal neurons infected with either scrambled, complete or partial shRNAs for ADAR2 knockdown (KD). (E) Quantification of results from D for four independent experiments. ****P<0.0001 (one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test). (F) Sanger sequencing chromatographs of the GluA2 PCR products from hippocampal neurons infected with either scrambled, complete or partial shRNAs for ADAR2 KD. Green arrows indicate the editing site. Only samples treated for complete ADAR2 knockdown show a dual A and G peak at the editing site. The green peak represents an A (unedited) base read and black represents a G (edited) base read.