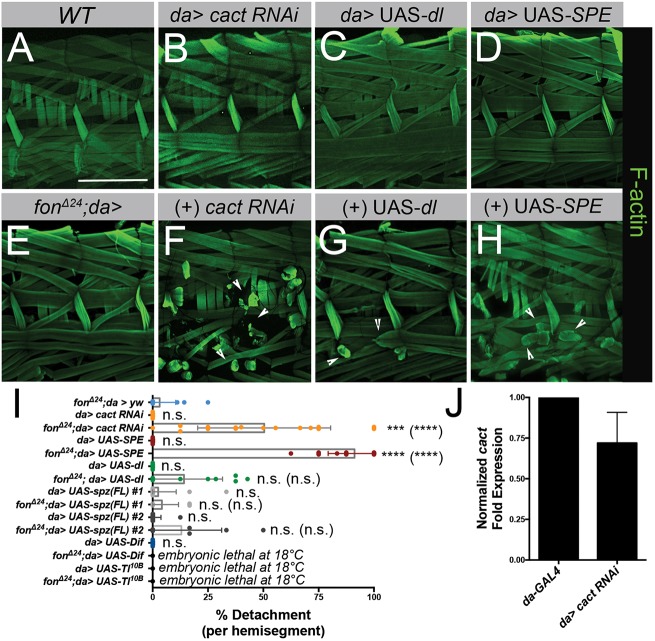
Fig. 5.
Genetic interactions between fon and Toll pathway components enhance muscle detachment. (A–H) Two hemisegments of muscle fillets stained with phalloidin (F-actin, green) in a wild-type control, candidate RNAi lines alone (B–D) or in the fon-sensitized genetic background, fonΔ24/+; da-GAL4 (E–H). (A,E) Morphological defects are absent in the muscles of wild-type and fonΔ24/+; da-GAL4 larval fillets. (B) RNAi knockdown of the NFκB inhibitor, cact, alone does not disrupt muscle attachment. (C,D) Overexpression of Dl or SPE has no obvious consequences for muscle attachment stability. (E–H) In comparison to heterozygous fonΔ24/+ alone (E), loss of cact (F) or the overexpression of dl (G) or SPE (H) in a fon-sensitized background enhances muscle detachment (arrowheads). (I) Mean±s.e.m quantification of muscle detachment of select genotypes (fonΔ24; da>yw, n=16; da>cact RNAi, n=12; fonΔ24; da>cact RNAi, n=21; da>UAS-SPE, n=20, fonΔ24; da>UAS-SPE, n=19; da>UAS-dl, n=10; fonΔ24; da>UAS-dl, n=13; da>UAS-spz(FL) #1, n=20; fonΔ24; da>UAS-spz(FL) #1, n=12); da>UAS-spz(FL) #2, n=17; fonΔ24; da>UAS-spz(FL) #2, n=10; da>UAS-Dif, n=16). Lethality of UAS-Dif and UAS-Toll10B combinations at and above 18°C prevented a similar larval analysis. Dots in each plot indicate results for individual larval fillet samples. (J) Mean±s.e.m effectiveness of RNAi knockdown of cact transcripts through cact RNAi #3 determined using qPCR. RNAi phenotypes of additional cact RNAi lines tested can be found in Fig. S5. P-values determined via Kruskal–Wallis statistical test; ***P<0.001; ****P<0.0001; n.s., not significant. P-values for comparisons to the sensitized background (fonΔ24; da>yw) alone are placed above each RNAi line. P-values of comparisons between RNAi alone and in combination with the sensitized background are denoted in parentheses. Scale bars: 500 µm.