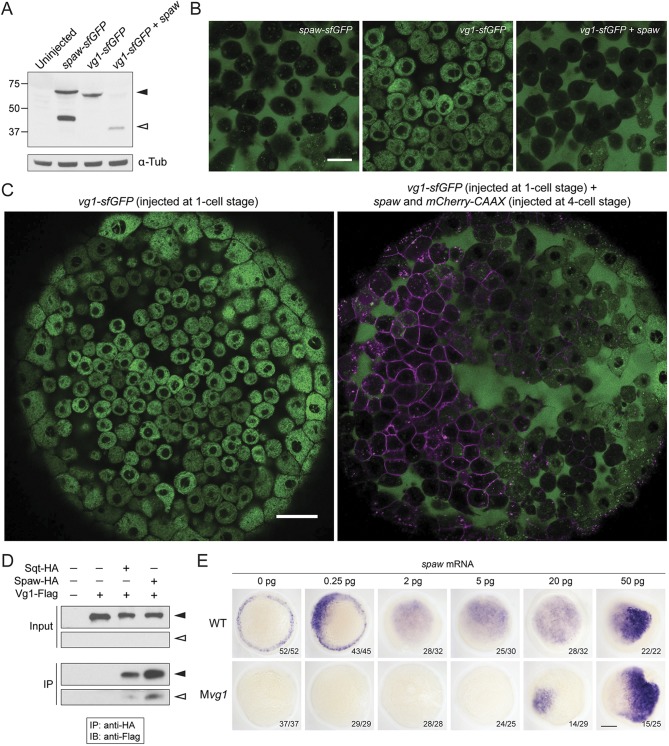
Fig. 2.
Spaw and Vg1/Gdf3 form heterodimers. (A) Anti-GFP reducing immunoblot of wild-type embryos injected with 25 pg of spaw-sfGFP, vg1-sfGFP or vg1-sfGFP and spaw mRNA. Black arrowhead indicates the position of full-length protein; open arrowhead represents cleaved protein. Lower panel: anti-α-Tubulin loading control. (B) Animal cap of sphere-stage live embryos injected at the one-cell stage with 50 pg of spaw-sfGFP, 50 pg of vg1-sfGFP mRNA or 50 pg of vg1-sfGFP and 50 pg of spaw mRNA. Scale bar: 20 µm. (C) Animal cap of a sphere-stage live embryo injected with 50 pg of vg1-sfGFP mRNA at the one-cell stage (left) or 50 pg of vg1-sfGFP mRNA at the one-cell stage and 25 pg of a spaw mRNA/mCherry-CAAX mRNA mix at the four-cell stage (right). Scale bar: 40 µm. (D) Anti-Flag reducing immunoblot (IB) of anti-HA immunoprecipitates (IPs) from lysates of wild-type embryos injected with 50 pg of squint-HA (sqt-HA), 50 pg of spaw-HA and/or 50 pg of vg1-Flag mRNA. Black arrowheads indicate the position of full-length protein; open arrowheads represent cleaved protein. The input and IP blots were exposed for different lengths of time. (E) Expression of lefty1 in wild-type and maternal vg1 (Mvg1) mutant embryos injected with 0.25-50 pg of spaw mRNA. Scale bar: 150 µm.