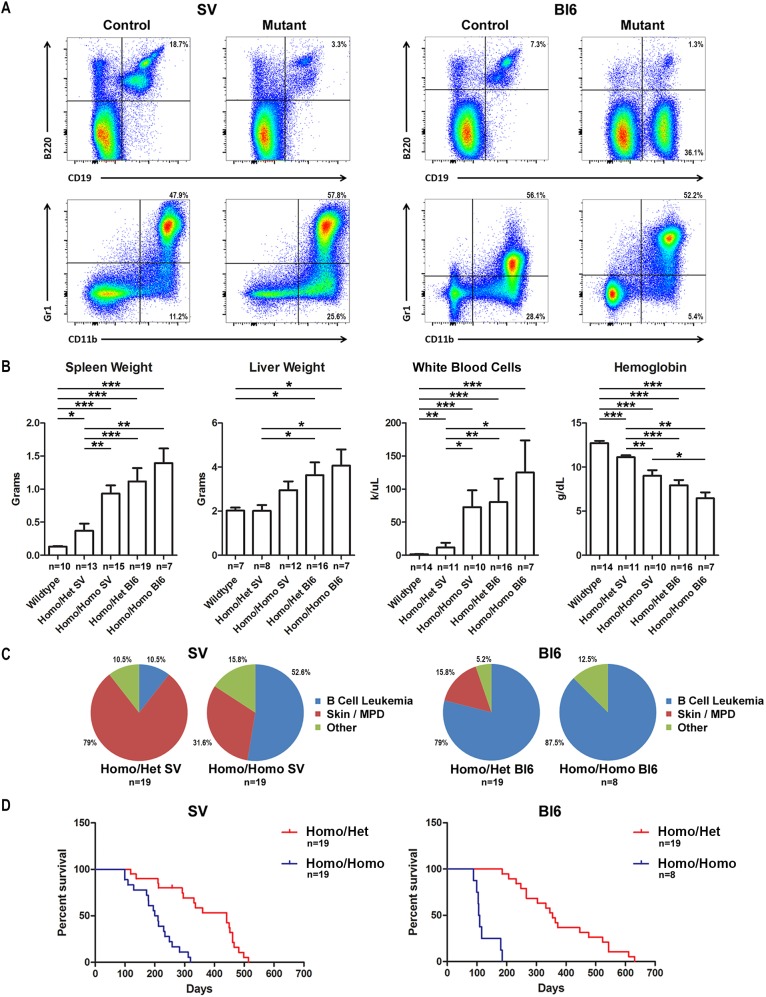
Fig. 1.
Deletion of RBP-J within renin cells of Bl6 and SV mice leads to B-cell leukemia and MPD, respectively. (A) Representative flow cytometry plots performed on the bone marrow of control and mutant mice from the SV (left panel) and Bl6 (right panel) background. Conditional deletion of RBP-J within renin cells of SV mice results in decreased number of CD19+B220+ B cells and an increase in CD11b+Gr1− and CD11b+Gr1+ myeloid cells. Conversely, conditional deletion of RBP-J within renin cells of Bl6 mice results in an aberrant population of CD19+B220dim leukemic B cells and a decrease in myeloid cells. (B) Mutant animals from the Bl6 background have increased spleen weight, liver weight and white blood cell count, as well as decreased hemoglobin, compared with mutant animals from the SV background. Further, mutant SV animals with two copies of Cre recombinase have increased spleen weight, increased white blood cell count and decreased hemoglobin compared with mutant SV animals with one copy of Cre recombinase. There was a trend towards worse disease in mutant Bl6 animals with two copies of Cre recombinase compared with Bl6 animals with one copy of Cre recombinase, although this was not statistically significant. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001, Mann–Whitney U-test. The sample size for each group is shown. (C) Animals with two copies of Cre recombinase (RBP-Jfl/fl;Ren1dCre/Cre) have a higher incidence of B-cell leukemia compared with mice with only one copy of Cre recombinase (RBP-Jfl/fl;Ren1dCre/+) for both the SV and Bl6 background. Mutant animals from the Bl6 background predominantly develop B-cell leukemia, whereas mutant animals from the SV background have a higher incidence of MPD (P<0.001, Fisher's exact test). The sample size for each group is shown. (D) In both SV and Bl6 mice, survival decreases in mutant animals with two copies of Cre recombinase (RBP-Jfl/fl;Ren1dCre/Cre) compared with those with only one copy (RBP-Jfl/fl;Ren1dCre/+). The sample size for each group is shown.