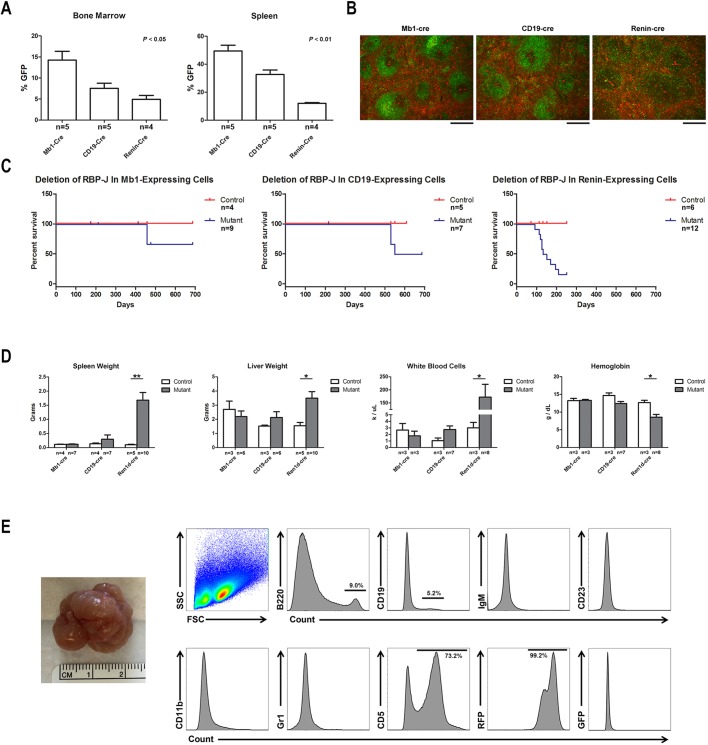
Fig. 5.
Renin-expressing cells are a susceptible population for malignant transformation. (A) Comparison of the expression pattern of different B-cell Cre recombinase transgenes – Mb1-Cre, CD19-Cre and renin-Cre – within the bone marrow and spleen by flow cytometry. Within the bone marrow and spleen, Mb1Cre;mTmG mice have the highest number of B cells that express GFP, followed by CD19Cre;mTmG and Ren1dCre;mTmG. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01, Kruskal–Wallis test. The sample size for each group is shown. (B) Cre-mediated GFP expression in the spleens of Mb1Cre;mTmG, CD19Cre;mTmG and Ren1dCre;mTmG mice. Scale bars: 200 µm. (C) Conditional deletion of RBP-J within renin-expressing cells leads to the development of B-cell leukemia and early death. However, conditional deletion of RBP-J within Mb1-expressing or CD19-expressing cells does not lead to B-cell leukemia. At advanced ages, 20% of RBP-Jdel/fl;Mb1Cre/+ mice and 50% of RBP-Jdel/fl;CD19Cre/+ mice developed abdominal tumors, leading to abdominal distension and death. The sample size for each group is shown. (D) Conditional deletion of RBP-J within renin-expressing cells, but not Mb1-expressing or CD19-expressing cells, resulted in elevated spleen weight, liver weight and white blood cell count and decreased hemoglobin compared with littermate control mice. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01, Mann–Whitney U-test. The sample size for each group is shown. (E) Representative tumor from RBP-Jdel/fl;CD19Cre/+ mice (leftmost). By flow cytometry analysis, abdominal tumors were positive for CD5 but negative for B-cell and myeloid markers. Further, the tumors were RFP+ and thus not due directly to deletion of RBP-J. FSC, forward scatter; SSC, side scatter.