Fig. 4.
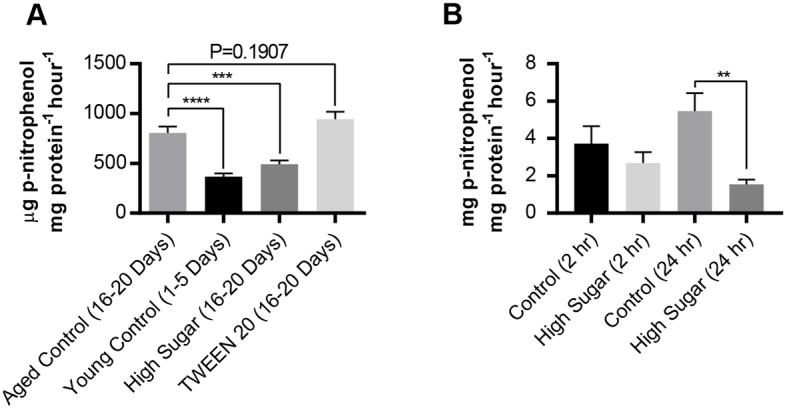
Dietary supplementation affects intestinal alkaline phosphatase (IAP) activity in adult flies and intestinal cell co-cultures. Alkaline phosphatase activity was tested using the substrate p-nitrophenol phosphate. (A) Gut lysates were tested after 3 weeks of feeding each additive (n=26 per diet). Error bars represent s.e.m. ***P<0.001; ****P<0.0001, compared to aged controls, using a one-way ANOVA. (B) Alkaline phosphatase assay for Caco-2/HT29-MTX cell monolayers exposed to control (5 mM glucose+20 mM mannitol) or high glucose (25 mM; HS) for 2 or 24 h (n=12). Error bars represent s.e.m. **P <0.01 using a two-tailed Mann–Whitney test.
