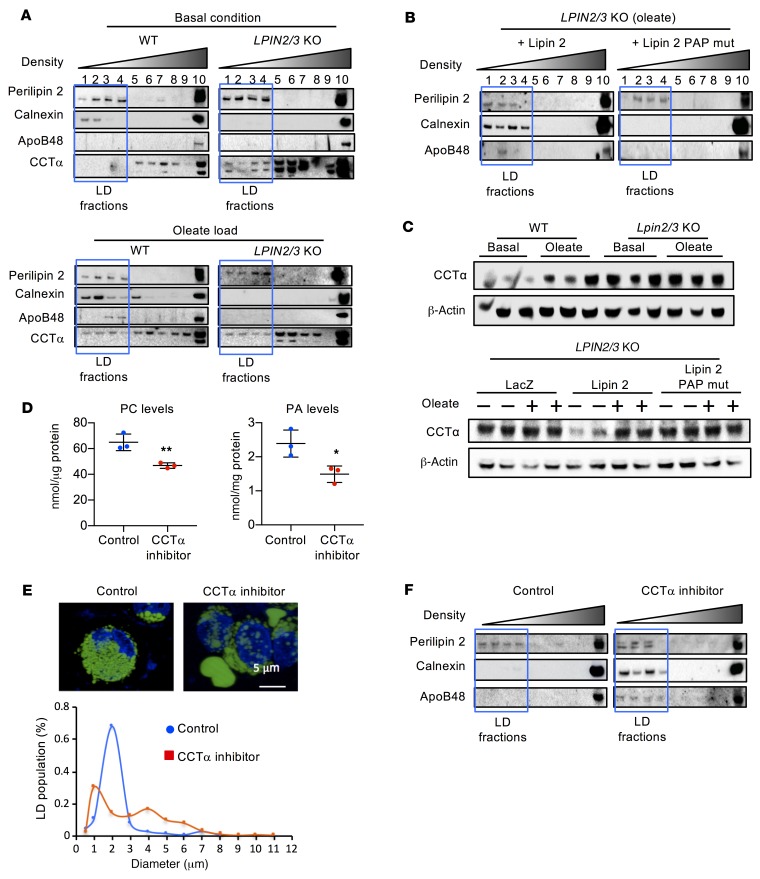
Figure 6. Lipin PAP activity is required for apoB48 association with lipid for chylomicron assembly.
(A) Analysis of apoB48 association with lipids by density gradient centrifugation followed by immunoblot to detect proteins across fractions. The lipid droplet–containing (LD-containing) fractions (outlined by blue box) were defined by the presence of perilipin 2. In WT cells, lipids were associated with the ER (calnexin), and apoB48 was present in LD fractions after oleate loading. In LPIN2/3-KO cells, neither apoB48 nor calnexin was present in LD fractions, even after oleate loading. Additionally, CCTα levels were elevated and appeared in the LD fractions even under basal conditions, which was not observed in WT cells. (B) Lipin PAP activity is required for apoB48 association with lipids in intestinal cells. LPIN2/3-KO cells were infected with adenovirus expressing WT lipin 2 or PAP-mutant lipin 2. Cells loaded with oleate were assessed for the presence of apoB48 in LD fractions. (C) Lipin PAP activity modulates CCTα protein levels. Elevated CCTα protein levels in LPIN2/3-KO cells under basal culture conditions are normalized by introduction of adenoviral vectors for WT, but not PAP-mutant, lipin 2. (D) CCTα inhibitor reduces PC and PA levels in WT HT-29 cells. Average ± SD, n = 3. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 by t test. (E) Fluorescence image (upper) and size distribution (lower) of LDs in LPIN2/3-KO HT-29 cells loaded with oleate without or with addition of CCTα inhibitor. n ≥ 30. Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). (F) CCTα inhibitor restores calnexin and apoB48 association with lipid-containing fractions from LPIN2/3-KO cells loaded with oleate. Blots shown throughout this figure are each representative of a single experiment, but the experiments in panels A–C and F are each variations of a similar experiment, such that in composite, the patterns for WT and Lpin2/3-KO mice were each replicated in at least 3 independent trials. Blots in A, C, and F were run with the same samples contemporaneously.