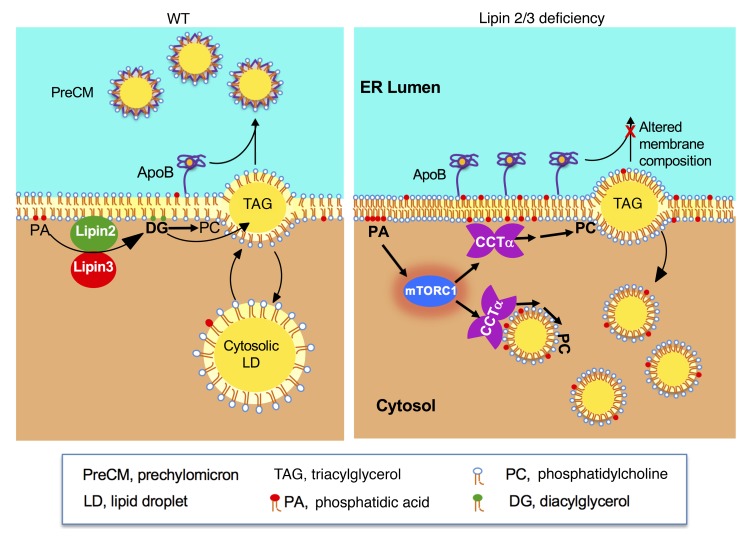
Figure 7. Proposed role of lipins 2 and 3 in intestinal chylomicron (CM) production.
Left: In WT enterocytes, TAG synthesized in the ER membrane may bud into the cytosol for storage as lipid droplets (LDs) or into the ER lumen to associate with apoB48 through the action of microsomal TAG transfer protein. The resulting prechylomicron particles (PreCMs) ultimately bud from the ER. In steps not shown, these lipoproteins subsequently mature in the Golgi and are released from enterocytes as mature CMs. Right: In the absence of lipin 2/3 PAP activity, the lipin substrate phosphatidic acid (PA) accumulates at membrane sites in the ER (and possibly additional cell membranes). Elevated PA may activate mTORC1, which enhances CCTα levels by increasing protein stability or translation. Increased CCTα contributes to elevated PC levels and altered membrane phospholipid composition and impaired PreCM formation. TAG-rich lipid droplets accumulate in the cytoplasm rather than contribute to CM formation.