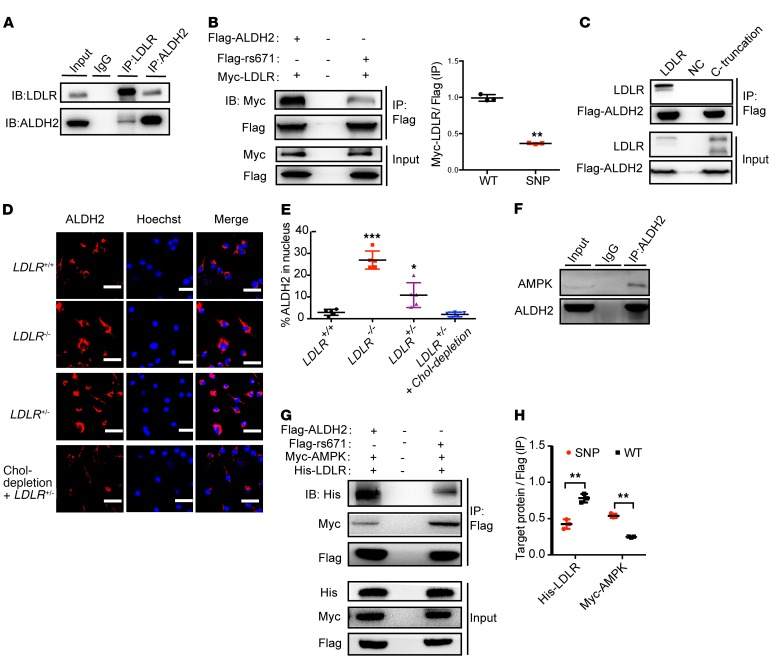
Figure 4. LDLR inhibits but ALDH2 rs671 mutant increases nuclear translocation of ALDH2 through interaction with AMPK.
(A) LDLR directly interacts with ALDH2 in BMDMs (n = 3). (B) ALDH2 rs671 mutant pulls down much less LDLR compared with WT ALDH2 (n = 3). (C) ALDH2 does not bind to LDLR when LDLR C-terminal is truncated (n = 3). (D and E) LDLR gene-dose–dependent inhibition of ALDH2 translocation. (D) LDLR upregulation decreased ALDH2 translocation by cholesterol depletion. Scale bars: 100 μm. Quantification is shown in E (n = 5). (F) ALDH2 directly binds to AMPK in LDLR-KO BMDMs. (G and H) ALDH2 rs671 mutant pulls down more AMPK compared with WT ALDH2 by cotransfection of Flag-tagged ALDH2, Myc-tagged AMPK, and His-tagged LDLR (G) and quantification (H, n = 3). Statistical comparisons were made using 2-tailed Student’s t test (B and H) or ANOVA (E). All data are mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.