Figure 1.
Statistics of the Clusters of Co-active and Contiguous ROIs
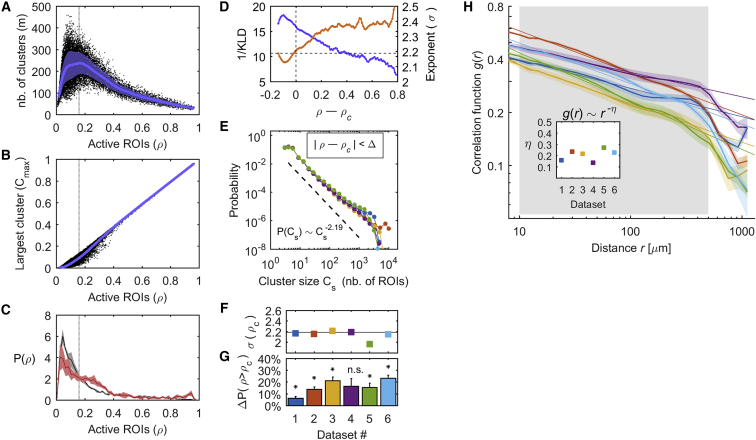
(A) Number of clusters (m) as a function of the proportion of active ROIs (ρ). Blue line, mean of m; blue area, its standard deviation.
(B) Normalized size of the largest cluster (Cmax) as a function of ρ (blue trace: average Cmax).
(C) Distribution of ρ (black, spontaneous activity; red, stimulus-evoked activity) calculated for each of the Q spontaneous and evoked segments (solid line, mean distribution; shaded area, SEM). Note that the stimulus-evoked distribution is skewed to the right.
(D) We calculated the cluster size distribution for the set of clusters that appeared with ρ comprised within small intervals (ρ – Δ; ρ + Δ). Using the Kullback-Leibler divergence (KLD), we calculated the goodness of fit of the power law (blue) and, using MLE, we estimated the power exponent (orange) as a function of ρ. (A)–(D) show results for dataset 1. Note that, for ρ = ρc, the goodness of fit is close to its maximum and the corresponding power exponent is equal to one predicted in the case of 3D percolation, equal to 2.19 (dashed horizontal line).
(E) Size distribution P(Cs) of clusters that appeared with ρ between ρc – Δ and ρc + Δ. Each color represents a dataset. Error bars are smaller than the symbols’ size. Black line, power-law distribution predicted in 3D percolation.
(F) Power exponents σ(ρc) estimated using MLE.
(G) Difference between the proportion of time that ρ > ρc during the stimulus-evoked activity and the proportion of time that ρ > ρc during the spontaneous activity (∗p < 0.01, paired t test). Error bars, SEM across the Q spontaneous-evoked segments. See also Figure S2.
(H) Correlation function g(r): average correlation between pairs of cells as a function of the Euclidean distance r, for each dataset (calculated for each of the Q segments and then averaged; colored areas, SEM). The straight lines represent power-law fits using least squares for r falling between 50 μm and 500 μm (gray area). Note that for distances longer than 500 μm, r approximates the size of the larva in one of its 3 dimensions.
Inset: estimated power-law exponent (estimation errors are smaller than the symbols’ size).