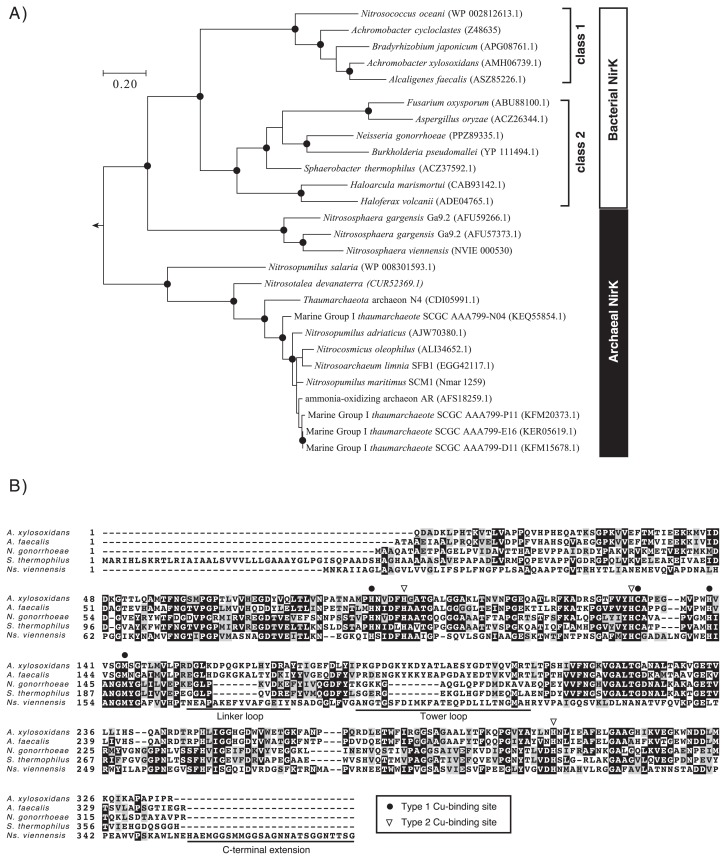
Fig. 1.
Phylogeny (A) and sequence alignments (B) of prokaryotic NirK. A) A phylogenetic tree of prokaryotic NirK was constructed by the maximum likelihood method with the Jones-Taylor-Thornton model using the protein sequence of multicopper oxidase type 3 of Nitrososphaera viennensis (accession number; AIC14243.1) as an outgroup. Branching points that support a probability >80% in bootstrap analyses (based on 500 replicates) are shown as filled circles. The scale bar represents 10% sequence divergence. Sequence accession numbers are indicated in parentheses. B) Protein sequence alignment of nirK. NirK sequences were aligned using ClustalW software. Circles and triangles correspond to the amino acid residues of type 1 and 2 Cu-binding sites, respectively. Linker, Tower loop (3), and C-terminal extension regions are underlined. Abbreviations of microorganisms are as follows: Nitrosomonas europaea is N. europaea, A. xylosoxidans is Achromobacter xylosoxidans, A. faecalis is Alcaligenes faecalis, N. gonorrhoeae is Neisseria gonorrhoeae, S. thermophilus is Sphaerobacter thermophilus, and Ns. viennensis is Nitrososphaera viennensis.